polity -Union Legislature-மத்திய நாடாளுமன்றம்
Quiz-summary (or) [Show All Quiz]
0 of 88 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
Information
polity -Union Legislature-மத்திய நாடாளுமன்றம் (PYQ)
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 88 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 88
1. Question
The whips in the Indian Parliament are appointed on the basis of
இந்திய பாராளுமன்றத்தில் கொறடாக்கள் நியமனம் செய்யப்படும் அடிப்படை (PYQ)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 2 of 88
2. Question
Which one of the following bills must be passed by each house of the Indian parliament separately by special majority?
கீழ்வரும் எந்த மசோதாவை பாராளுமன்றத்தில் தனித்தனியாக கொண்டு வந்து பெரும்பான்மை வாக்கு பெற வேண்டும்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 3 of 88
3. Question
Rajya Sabha consists of not more than ———— members
மாநிலங்கள் அவை ———— க்கு மிகாத உறுப்பினர்களை கொண்டுள்ளது(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 4 of 88
4. Question
How many days money bills can delayed by the Rajya Sabha
நிதி மசோதாக்கள் மாநில அவையினால் எத்தனை நாட்கள் தாமதப்படுத்தலாம்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 5 of 88
5. Question
Rajya Sabha consists of ———— members
தற்போதைய மாநிலங்களவை உறுப்பினர்களின் எண்ணிக்கை(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 6 of 88
6. Question
Which one of the following provisions can be amended by a simple majority in the parliament?
பின்வரும் விதிமுறைகளில் எந்த ஒன்று பாராளுமன்றத்தின் சாதாரண பெரும்பான்மை மூலம் நிறைவேற்றப்பட இயலும்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 7 of 88
7. Question
How many times does the parliament meet in a year normally?
நடைமுறையில் நாடாளுமன்றம் ஆண்டிற்கு எத்தனை முறை கூட்டப்படுகிறது?(PYQ)Correct
இந்திய நாடாளுமன்றம் பொதுவாக வருடத்திற்கு மூன்று அமர்வுகளுக்கு கூடுகிறது . அவை
- பட்ஜெட் கூட்டத்தொடர் (பிப்ரவரி-மே),
- மழைக்கால கூட்டத்தொடர் (ஜூலை-செப்டம்பர்) மற்றும்
- குளிர்கால கூட்டத்தொடர் (நவம்பர்-டிசம்பர்) ஆகும்.
அரசியலமைப்புச் சட்டம், நாடாளுமன்றம் வருடத்திற்கு இரண்டு முறையாவது கூட வேண்டும் என்றும், அமர்வுகளுக்கு இடையே ஆறு மாதங்களுக்கு மேல் இடைவெளி இருக்கக்கூடாது என்றும் கூறுகிறது.
The Indian Parliament typically meets for three sessions per year. These are- the Budget Session (February-May),
- the Monsoon Session (July-September),
- and the Winter Session (November-December).
The Constitution mandates that Parliament must meet at least twice a year, and there cannot be more than a six-month gap between sessions.Incorrect
இந்திய நாடாளுமன்றம் பொதுவாக வருடத்திற்கு மூன்று அமர்வுகளுக்கு கூடுகிறது . அவை
- பட்ஜெட் கூட்டத்தொடர் (பிப்ரவரி-மே),
- மழைக்கால கூட்டத்தொடர் (ஜூலை-செப்டம்பர்) மற்றும்
- குளிர்கால கூட்டத்தொடர் (நவம்பர்-டிசம்பர்) ஆகும்.
அரசியலமைப்புச் சட்டம், நாடாளுமன்றம் வருடத்திற்கு இரண்டு முறையாவது கூட வேண்டும் என்றும், அமர்வுகளுக்கு இடையே ஆறு மாதங்களுக்கு மேல் இடைவெளி இருக்கக்கூடாது என்றும் கூறுகிறது.
The Indian Parliament typically meets for three sessions per year. These are- the Budget Session (February-May),
- the Monsoon Session (July-September),
- and the Winter Session (November-December).
The Constitution mandates that Parliament must meet at least twice a year, and there cannot be more than a six-month gap between sessions. -
Question 8 of 88
8. Question
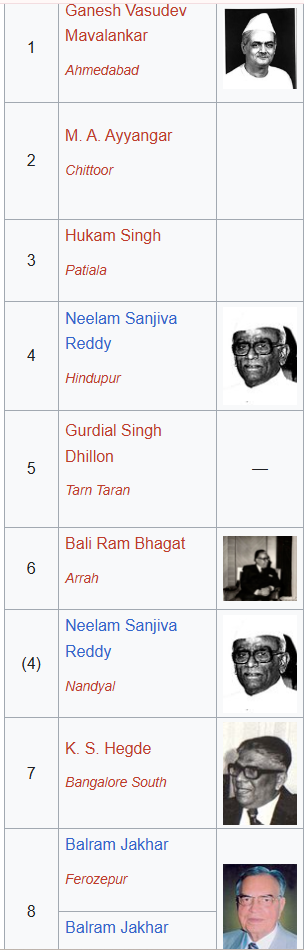
Who was the speaker of the Eleventh Lok Sabha?
பதினோறாவது மக்களவையின் சபாநாயகர் யார்?(PYQ)Correct
-
Ganesh Vasudev Mavalankar served as the speaker from 15th May 1952 to 27th February 1956.
-
The second speaker was M.A. Ayyangar from 8th March 1956 to 10th May 1957. He continued to be the speaker from 11th May 1957 to 16th April 1962.
-
The third speaker was Sardar Hukam Singh who served as the speaker from 17th April 1962 to 16th March 1967.
-
The fourth speaker was Neelam Sanjiva Reddy who served from 17th March 1967 to 19th July 1971.
-
The fifth was Gurdial Singh Dhillion serving as the speaker of Lok Sabha from 8th August 1969 to 19th March 1971 and continuing his position from 22nd March 1971 to 1st December 1975.
-
The sixth speaker was Bali Ram Bhagat who served from 15th January 1976 to 25th March 1977.
-
After him, Neelam Sanjiva was again elected as the speaker serving from 26th March 1977 to 13th July 1977 as the 7th speaker of the House of People.
-
The 8th speaker was K.S. Hegde served from 21st July 1977 to 21st January 1980.
-
The 9th speaker was Balram Jakhar who served from the year 1980 22nd January to 1985 15th January. He again continued to be the speaker from 16th January 1985 to 18th December 1989.
-
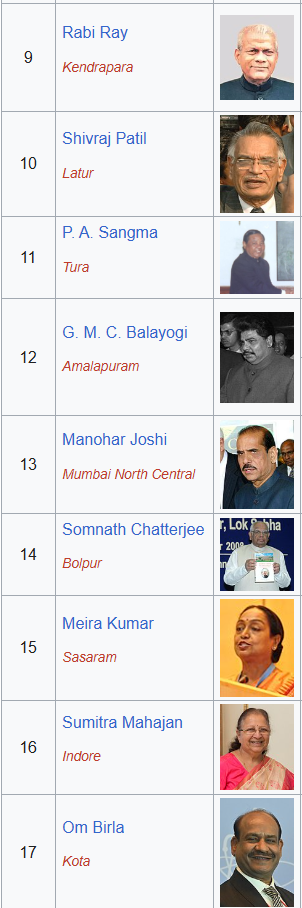
The 10th speaker of the House of People was Rabi Ray who served from 19th December 1989 to 9th July 1991.
-
The 11th speaker was Shivraj Patil serving as the speaker of Lok Sabha from 10th July 1991 to 22nd May 1996.
-
the 12th speaker was P. A Sangma serving from the year 1996 23rd May to 23rd March 1998.
-
After that G.M.C. Balayogi continued to be the 12th speaker of Lok Sabha and served from 24th March 1998 to 19th October 1999. He then continued from the year 1999 22nd October to 3rd March 2002.
-
The 13th Speaker was Manohar Joshi who served from the year 10th May 2002 to 2nd June 2004.
-
The 14th speaker was Somnath Chatterjee serving from 4th June 2004 to 30th May 2009.
-
The 15th speaker was Meira Kumar serving from 30th May 2009 to 4th June 2014.
-
The 16th speaker was Sumitra Mahajan serving from 6th June 2014 to 16th June 2019.
-
The 17th speaker – Om Birla.
- The 18th speaker – Om Birla. (now 2025)
Incorrect
-
Ganesh Vasudev Mavalankar served as the speaker from 15th May 1952 to 27th February 1956.
-
The second speaker was M.A. Ayyangar from 8th March 1956 to 10th May 1957. He continued to be the speaker from 11th May 1957 to 16th April 1962.
-
The third speaker was Sardar Hukam Singh who served as the speaker from 17th April 1962 to 16th March 1967.
-
The fourth speaker was Neelam Sanjiva Reddy who served from 17th March 1967 to 19th July 1971.
-
The fifth was Gurdial Singh Dhillion serving as the speaker of Lok Sabha from 8th August 1969 to 19th March 1971 and continuing his position from 22nd March 1971 to 1st December 1975.
-
The sixth speaker was Bali Ram Bhagat who served from 15th January 1976 to 25th March 1977.
-
After him, Neelam Sanjiva was again elected as the speaker serving from 26th March 1977 to 13th July 1977 as the 7th speaker of the House of People.
-
The 8th speaker was K.S. Hegde served from 21st July 1977 to 21st January 1980.
-
The 9th speaker was Balram Jakhar who served from the year 1980 22nd January to 1985 15th January. He again continued to be the speaker from 16th January 1985 to 18th December 1989.
-
The 10th speaker of the House of People was Rabi Ray who served from 19th December 1989 to 9th July 1991.
-
The 11th speaker was Shivraj Patil serving as the speaker of Lok Sabha from 10th July 1991 to 22nd May 1996.
-
the 12th speaker was P. A Sangma serving from the year 1996 23rd May to 23rd March 1998.
-
After that G.M.C. Balayogi continued to be the 12th speaker of Lok Sabha and served from 24th March 1998 to 19th October 1999. He then continued from the year 1999 22nd October to 3rd March 2002.
-
The 13th Speaker was Manohar Joshi who served from the year 10th May 2002 to 2nd June 2004.
-
The 14th speaker was Somnath Chatterjee serving from 4th June 2004 to 30th May 2009.
-
The 15th speaker was Meira Kumar serving from 30th May 2009 to 4th June 2014.
-
The 16th speaker was Sumitra Mahajan serving from 6th June 2014 to 16th June 2019.
-
The 17th speaker – Om Birla.
- The 18th speaker – Om Birla. (now 2025)
-
Question 9 of 88
9. Question
Who was the Prime Minister when for the first time a No-confidence motion was moved in the Indian Parliament?
நம்பிக்கையில்லா தீர்மானம் முதன் முதலாக இந்திய நாடாளுமன்றத்தில் கொண்டு வந்த பொழுது பிரதம அமைச்சராக இருந்தவர் யார்?(PYQ)Correct
J. B. Kripalani moved the first-ever no-confidence motion on the floor of the Lok Sabha against the government of prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru in August 1963, immediately after the disastrous Sino-Indian War. As of August 2023, 31 no-confidence motions have been moved.
சீன-இந்தியப் போருக்குப் பிறகு, ஆகஸ்ட் 1963 இல், பிரதமர் ஜவஹர்லால் நேருவின் அரசாங்கத்திற்கு எதிராக, மக்களவையில் ஜே.பி. கிருபளானி முதல் நம்பிக்கையில்லா தீர்மானத்தை கொண்டு வந்தார்.
A motion of “No Confidence” against the Government can be introduced only in the Lok Sabha under Rule 198.
History of no confidence motion (NCM)
- First NCM – It was during the 3rd Lok Sabha in 1963 that the first motion of no confidence was moved by Acharya J B Kripalani against the government headed by Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Highest number of instances–
- Indira Gandhi- Faced NCMs 15 times.
- Lal Bahadur Shasthri- Faced 3 times.
- PV Narashima Rao- Faced three times.
- In 1979, Prime Minister Morarji Desai realised that he did not have the support of the majority of MPs, and therefore resigned before the House voted on the motion.
- Governments fallen due to NCM
- V P Singh government in 1990
- H D Deve Gowda government in 1997
- Atal Bihari Vajpayee government in 1999
Incorrect
J. B. Kripalani moved the first-ever no-confidence motion on the floor of the Lok Sabha against the government of prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru in August 1963, immediately after the disastrous Sino-Indian War. As of August 2023, 31 no-confidence motions have been moved.
சீன-இந்தியப் போருக்குப் பிறகு, ஆகஸ்ட் 1963 இல், பிரதமர் ஜவஹர்லால் நேருவின் அரசாங்கத்திற்கு எதிராக, மக்களவையில் ஜே.பி. கிருபளானி முதல் நம்பிக்கையில்லா தீர்மானத்தை கொண்டு வந்தார்.
A motion of “No Confidence” against the Government can be introduced only in the Lok Sabha under Rule 198.
History of no confidence motion (NCM)
- First NCM – It was during the 3rd Lok Sabha in 1963 that the first motion of no confidence was moved by Acharya J B Kripalani against the government headed by Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Highest number of instances–
- Indira Gandhi- Faced NCMs 15 times.
- Lal Bahadur Shasthri- Faced 3 times.
- PV Narashima Rao- Faced three times.
- In 1979, Prime Minister Morarji Desai realised that he did not have the support of the majority of MPs, and therefore resigned before the House voted on the motion.
- Governments fallen due to NCM
- V P Singh government in 1990
- H D Deve Gowda government in 1997
- Atal Bihari Vajpayee government in 1999
-
Question 10 of 88
10. Question
How many members are elected from Tamil Nadu to Rajya Sabha?
ராஜ்ய சபாவிற்கு தமிழ்நாட்டிலிருந்து எத்தனை உறுப்பினர்கள் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார்கள்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 11 of 88
11. Question
When was the office of Cabinet Secretary created in India?
எந்த ஆண்டு கேபினேட் செயலாளர் பதவி இந்தியாவில் உருவாக்கப்பட்டது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 12 of 88
12. Question
Which of the following statements on Rajya Sabha is not true?
இராஜ்ய சபாவைப் பற்றி பின்வரும் கூற்றுகளில் தவறானது எது?(PYQ)Correct
மாநிலங்களவை உறுப்பினரின் பதவிக்காலம் ஆறு ஆண்டுகள் ஆகும். மேலவையின் மூன்றில் இரண்டு பங்கு (2/3) உறுப்பினர்களின் பதவிக்காலம் ஒவ்வொரு இரண்டு ஆண்டுகளுக்கு ஒருமுறை முடிவடையும். மாநிலங்களவைத் தலைவராக குடியரசுத் துணைத்தலைவர் பதவி வகிப்பார்.
Incorrect
மாநிலங்களவை உறுப்பினரின் பதவிக்காலம் ஆறு ஆண்டுகள் ஆகும். மேலவையின் மூன்றில் இரண்டு பங்கு (2/3) உறுப்பினர்களின் பதவிக்காலம் ஒவ்வொரு இரண்டு ஆண்டுகளுக்கு ஒருமுறை முடிவடையும். மாநிலங்களவைத் தலைவராக குடியரசுத் துணைத்தலைவர் பதவி வகிப்பார்.
-
Question 13 of 88
13. Question
Lok Sabha consists of
மக்களவையின் மொத்த உறுப்பினர்களின் எண்ணிக்கை(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 14 of 88
14. Question
Money bills can be delayed by the Rajya Sabha
பண மசோதாக்கள் ராஜ்ய சபாவில் எத்தனை நாட்கள் காலதாமதபடுத்தப்படும்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 15 of 88
15. Question
Which amendment restricted the total size of council of ministers to 15% the total strength of Lok Sabha?
எந்த அரசியலமைப்பு திருத்தம் மந்திரி சபையின் மொத்த அளவை மக்களவையின் பலத்தில் 15 சதவீதம் தான் அதிகபட்சம் இருக்க வகை செய்துள்ளது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 16 of 88
16. Question
Which of the following is/are true?
I) The Council of Ministers shall be collectively responsible to the House of the people.
II) The Ministers are individually responsible to the executive head.
III) The Ministers shall hold office during the pleasure of the President.
IV) The Council of Minister shall be collectively responsible to the Prime Minister.
கீழ்கண்டவற்றுள் சரியானவை எவை?(PYQ)
I) அமைச்சரவை கூட்டாக மக்களவைக்கு பொறுப்புடையதாகும்.
II) அமைச்சர்கள் தனிப்பட்ட முறையில் நிர்வாகத் தலைமைக்கு பொறுப்புடையவர்கள் ஆவார்கள்.
III) குடியரசுத் தலைவர் விரும்பும் வரை அமைச்சர்கள் பதவி வகிப்பார்கள்.
IV) அமைச்சரவை கூட்டாக பிரதம அமைச்சருக்கு பொறுப்புடையதாகும்Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 17 of 88
17. Question
How many days may a member of Parliament be absent from sittings of his house without permission?
ஒரு பாராளுமன்ற உறுப்பினர் அனுமதி பெறாமல் எத்தனை நாட்களுக்கு அவை நடவடிக்கைகளில் கலந்து கொள்ளாமல் இருக்கலாம்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 18 of 88
18. Question
The Presiding Officers of both the Houses of Parliament allows the members to speak in
பாராளுமன்றத்தில் தலைமை அதிகாரி இரு அவைகளைப் பற்றி பேசுவதற்கு அனுமதிக்கப்படுகின்ற மொழிகள் யாவை?(PYQ)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 19 of 88
19. Question
Which of the following is/are not the main features of the parliamentary system of government?
1) Fusion of powers
2) Judicial review
3) Written constitutionபின்வருவனவற்றுள் பாராளுமன்ற முறையின்படி தவறான கூற்று எது?(PYQ)
1) அதிகார ஒருங்கிணைப்பு
2) நீதி மறு ஆய்வு
3) எழுதப்பட்ட அரசியல் சட்டம்Correct
நாடாளுமன்ற அரசாங்கத்தின் அம்சங்கள்
- பெயரளவு மற்றும் உண்மையான நிர்வாகிகள்: ஜனாதிபதி பெயரளவு நிர்வாகி (சட்டப்பூர்வ அல்லது பெயரளவு நிர்வாகி என்றும் அழைக்கப்படுகிறது), அதே நேரத்தில் பிரதமர் உண்மையான நிர்வாகி (நடைமுறை நிர்வாகி). இதன் விளைவாக, ஜனாதிபதி மாநிலத்தின் தலைவராகவும், பிரதமர் அரசாங்கத்தின் பிரதமராகவும் உள்ளார்.
- இரட்டை உறுப்பினர் பதவி: பிரதமரும் அமைச்சர்கள் குழுவும் நிர்வாகத் துறையாகவும், நாடாளுமன்றம் சட்டமன்றத் துறையாகவும் செயல்படுகின்றன. நாடாளுமன்ற உறுப்பினர்கள் பிரதமரையும் அமைச்சர்களையும் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கிறார்கள், அதாவது நிர்வாகத் துறை சட்டமன்றத்திலிருந்து வருகிறது.
- கூட்டுப் பொறுப்பு: நிர்வாகத்திற்கு சட்டமன்றத்திற்கு ஒரு கூட்டுப் பொறுப்பு உள்ளது. ஒரு கூட்டுப் பொறுப்பு உள்ளது, அதாவது ஒவ்வொரு அமைச்சரின் பொறுப்புகளும் முழு கவுன்சிலாலும் பகிர்ந்து கொள்ளப்படுகின்றன.
- நடைமுறை ரகசியம்: இந்த வகையான நிர்வாகத்தின் ஒரு தேவை என்னவென்றால், அமைச்சரவை நடவடிக்கைகள் ரகசியமாக வைக்கப்பட வேண்டும், பகிரங்கப்படுத்தப்படக்கூடாது.
- பிரதம மந்திரி தலைமைத்துவம்: இந்த நிர்வாக முறைக்கு பிரதமர் பொறுப்பேற்கிறார்.
- பெரும்பான்மை கட்சி விதி: பிரதம மந்திரி பொதுவாக கீழ் சபையில் பெரும்பான்மை பெறும் கட்சியின் தலைவரால் நியமிக்கப்படுவார்.
- இரு அவை சட்டமன்றம்: பெரும்பாலான நாடாளுமன்ற ஜனநாயக நாடுகளில் இரு அவை சட்டமன்றங்கள் பயன்படுத்தப்படுகின்றன.
- அரசியல் ஒருமைப்பாடு: அமைச்சர்கள் குழுவின் உறுப்பினர்கள் பொதுவாக ஒரே அரசியல் கட்சியைச் சேர்ந்தவர்கள், எனவே அவர்கள் ஒத்த அரசியல் சித்தாந்தங்களைக் கொண்டுள்ளனர். கூட்டணி அரசாங்கத்தில் உள்ள அமைச்சர்கள் ஒருமித்த கருத்துக்குக் கட்டுப்பட்டவர்கள்.
- நிலையான பதவிக்காலம் இல்லை: அரசாங்கத்தின் பதவிக்காலம் கீழ் சபையின் பெரும்பான்மை ஆதரவால் தீர்மானிக்கப்படுகிறது. அரசாங்கம் நம்பிக்கையில்லா வாக்கெடுப்பில் வெற்றி பெறத் தவறினால் அமைச்சர்கள் குழு ராஜினாமா செய்ய வேண்டும். தேர்தல்கள் நடத்தப்பட்டு புதிய அரசாங்கம் அமைக்கப்படும்.
நாடாளுமன்ற அமைப்பின் சிறப்புகள்
- நிர்வாகத்திற்கும் சட்டமன்றத்திற்கும் இடையே சிறந்த ஒருங்கிணைப்பு: நிர்வாகம் சட்டமன்றத்தின் ஒரு பகுதியாக இருப்பதாலும், பெரும்பாலான சட்டமன்றங்கள் பொதுவாக அரசாங்கத்தை ஆதரிப்பதாலும், சட்டங்களை இயற்றுவதும் அவற்றை செயல்படுத்துவதும் எளிதானது.
- சர்வாதிகாரத்தைத் தடுத்தல்: நிர்வாகக் கிளை சட்டமன்றத்திற்குப் பொறுப்புக்கூற வேண்டியிருப்பதாலும், நம்பிக்கையில்லாத் தீர்மானங்கள் மூலம் அதற்கு எதிராக வாக்களிக்க முடியும் என்பதாலும், சர்வாதிகாரம் இல்லை. மேலும், ஜனாதிபதி முறையைப் போலன்றி, அதிகாரம் ஒரு கையில் குவிந்துவிடாது.
- பொறுப்புள்ள அரசாங்கம்: அமைச்சர்கள் தங்கள் செயல்களுக்கு நாடாளுமன்றத்திற்குக் கணக்குக் கொடுக்க வேண்டும். கேள்வி நேரம், ஒத்திவைப்புத் தீர்மானம், நம்பிக்கையில்லாத் தீர்மானம் போன்ற பல்வேறு சாதனங்கள் மூலம் நாடாளுமன்றம் நிர்வாகத்தின் மீது கட்டுப்பாட்டைப் பயன்படுத்துகிறது.
- மாற்று அரசாங்கம் தயார் : ஆளும் கட்சி பெரும்பான்மையை இழந்தால், ஜனாதிபதி எதிர்க்கட்சியை அரசாங்கத்தை அமைக்க அழைக்கலாம். எனவே புதிய தேர்தல்கள் இல்லாமல் மாற்று அரசாங்கத்தை அமைக்க முடியும்.
- பல்வேறு குழுக்களின் பிரதிநிதித்துவம்: இந்த அமைப்பில், நாடாளுமன்றம் நாட்டில் உள்ள பல்வேறு குழுக்களுக்கு பிரதிநிதித்துவத்தை வழங்குகிறது. இது இந்தியா போன்ற நாடுகளுக்கு மிகவும் முக்கியமானது.
- நெகிழ்வுத்தன்மை : தேவைக்கேற்ப PM-ஐ எளிதாக மாற்ற முடியும் என்பதால் இந்த அமைப்பு நெகிழ்வானது.
Features of Parliamentary Government
- Nominal and Real Executives: The President is the nominal executive (also known as the de jure or titular executive), whereas the Prime Minister is the real executive (de facto executive). As a result, the President is the President of the State, whereas the Prime Minister is the Prime Minister of the Government.
- Double Membership: The Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers serve as the executive, while the Parliament serves as the legislature. Members of parliament elect the Prime Minister and ministers, meaning that the executive comes from the legislative.
- Collective Responsibility: The executive has a collective responsibility to the legislative. There is a collective responsibility, which means that each minister’s responsibilities are shared by the entire Council.
- Secrecy of procedure: A requirement of this type of administration is that cabinet proceedings be kept secret and not made public.
- Prime Ministerial Leadership: The Prime Minister is in charge of this system of administration.
- Majority Party Rule: The Prime Minister is usually appointed by the leader of the party that obtains a majority in the lower chamber.
- Bicameral Legislature: Bicameral legislatures are used in most parliamentary democracies.
- Political Homogeneity: Members of the Council of Ministers are usually from the same political party, and so have similar political ideologies. The ministers in a coalition government are bound by consensus.
- No fixed term: The government’s term is determined by the lower house’s majority support. The council of ministers must resign if the government fails to win a vote of no confidence. There will be elections, and a new government will be formed.
Merits of Parliamentary System
- Better coordination between the administration and the legislature: Since the administration is part of the legislature, and most legislatures generally support the government, it is easier to pass laws and implement them.
- Prevent authoritarianism: since the executive branch is accountable to the legislature and can vote against it with motions of no confidence, there is no authoritarianism. Also, unlike a presidential system, power will not be concentrated in one hand.
- Responsible government: Ministers are accountable to Parliament for their actions. Parliament exercises control over the executive through various devices like question hour, adjournment motion, no-confidence motion etc.
- Ready Alternative Government: If a ruling party loses the majority, president can invite the opposition party to form the government. Therefore alternative government can be formed without fresh elections.
- Representation of different groups: In this system, the parliament provides representation for different groups in the country. This is especially important for countries like India.
- Flexibility: The system is flexible because the PM can be easily changed as needed.
Incorrect
நாடாளுமன்ற அரசாங்கத்தின் அம்சங்கள்
- பெயரளவு மற்றும் உண்மையான நிர்வாகிகள்: ஜனாதிபதி பெயரளவு நிர்வாகி (சட்டப்பூர்வ அல்லது பெயரளவு நிர்வாகி என்றும் அழைக்கப்படுகிறது), அதே நேரத்தில் பிரதமர் உண்மையான நிர்வாகி (நடைமுறை நிர்வாகி). இதன் விளைவாக, ஜனாதிபதி மாநிலத்தின் தலைவராகவும், பிரதமர் அரசாங்கத்தின் பிரதமராகவும் உள்ளார்.
- இரட்டை உறுப்பினர் பதவி: பிரதமரும் அமைச்சர்கள் குழுவும் நிர்வாகத் துறையாகவும், நாடாளுமன்றம் சட்டமன்றத் துறையாகவும் செயல்படுகின்றன. நாடாளுமன்ற உறுப்பினர்கள் பிரதமரையும் அமைச்சர்களையும் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கிறார்கள், அதாவது நிர்வாகத் துறை சட்டமன்றத்திலிருந்து வருகிறது.
- கூட்டுப் பொறுப்பு: நிர்வாகத்திற்கு சட்டமன்றத்திற்கு ஒரு கூட்டுப் பொறுப்பு உள்ளது. ஒரு கூட்டுப் பொறுப்பு உள்ளது, அதாவது ஒவ்வொரு அமைச்சரின் பொறுப்புகளும் முழு கவுன்சிலாலும் பகிர்ந்து கொள்ளப்படுகின்றன.
- நடைமுறை ரகசியம்: இந்த வகையான நிர்வாகத்தின் ஒரு தேவை என்னவென்றால், அமைச்சரவை நடவடிக்கைகள் ரகசியமாக வைக்கப்பட வேண்டும், பகிரங்கப்படுத்தப்படக்கூடாது.
- பிரதம மந்திரி தலைமைத்துவம்: இந்த நிர்வாக முறைக்கு பிரதமர் பொறுப்பேற்கிறார்.
- பெரும்பான்மை கட்சி விதி: பிரதம மந்திரி பொதுவாக கீழ் சபையில் பெரும்பான்மை பெறும் கட்சியின் தலைவரால் நியமிக்கப்படுவார்.
- இரு அவை சட்டமன்றம்: பெரும்பாலான நாடாளுமன்ற ஜனநாயக நாடுகளில் இரு அவை சட்டமன்றங்கள் பயன்படுத்தப்படுகின்றன.
- அரசியல் ஒருமைப்பாடு: அமைச்சர்கள் குழுவின் உறுப்பினர்கள் பொதுவாக ஒரே அரசியல் கட்சியைச் சேர்ந்தவர்கள், எனவே அவர்கள் ஒத்த அரசியல் சித்தாந்தங்களைக் கொண்டுள்ளனர். கூட்டணி அரசாங்கத்தில் உள்ள அமைச்சர்கள் ஒருமித்த கருத்துக்குக் கட்டுப்பட்டவர்கள்.
- நிலையான பதவிக்காலம் இல்லை: அரசாங்கத்தின் பதவிக்காலம் கீழ் சபையின் பெரும்பான்மை ஆதரவால் தீர்மானிக்கப்படுகிறது. அரசாங்கம் நம்பிக்கையில்லா வாக்கெடுப்பில் வெற்றி பெறத் தவறினால் அமைச்சர்கள் குழு ராஜினாமா செய்ய வேண்டும். தேர்தல்கள் நடத்தப்பட்டு புதிய அரசாங்கம் அமைக்கப்படும்.
நாடாளுமன்ற அமைப்பின் சிறப்புகள்
- நிர்வாகத்திற்கும் சட்டமன்றத்திற்கும் இடையே சிறந்த ஒருங்கிணைப்பு: நிர்வாகம் சட்டமன்றத்தின் ஒரு பகுதியாக இருப்பதாலும், பெரும்பாலான சட்டமன்றங்கள் பொதுவாக அரசாங்கத்தை ஆதரிப்பதாலும், சட்டங்களை இயற்றுவதும் அவற்றை செயல்படுத்துவதும் எளிதானது.
- சர்வாதிகாரத்தைத் தடுத்தல்: நிர்வாகக் கிளை சட்டமன்றத்திற்குப் பொறுப்புக்கூற வேண்டியிருப்பதாலும், நம்பிக்கையில்லாத் தீர்மானங்கள் மூலம் அதற்கு எதிராக வாக்களிக்க முடியும் என்பதாலும், சர்வாதிகாரம் இல்லை. மேலும், ஜனாதிபதி முறையைப் போலன்றி, அதிகாரம் ஒரு கையில் குவிந்துவிடாது.
- பொறுப்புள்ள அரசாங்கம்: அமைச்சர்கள் தங்கள் செயல்களுக்கு நாடாளுமன்றத்திற்குக் கணக்குக் கொடுக்க வேண்டும். கேள்வி நேரம், ஒத்திவைப்புத் தீர்மானம், நம்பிக்கையில்லாத் தீர்மானம் போன்ற பல்வேறு சாதனங்கள் மூலம் நாடாளுமன்றம் நிர்வாகத்தின் மீது கட்டுப்பாட்டைப் பயன்படுத்துகிறது.
- மாற்று அரசாங்கம் தயார் : ஆளும் கட்சி பெரும்பான்மையை இழந்தால், ஜனாதிபதி எதிர்க்கட்சியை அரசாங்கத்தை அமைக்க அழைக்கலாம். எனவே புதிய தேர்தல்கள் இல்லாமல் மாற்று அரசாங்கத்தை அமைக்க முடியும்.
- பல்வேறு குழுக்களின் பிரதிநிதித்துவம்: இந்த அமைப்பில், நாடாளுமன்றம் நாட்டில் உள்ள பல்வேறு குழுக்களுக்கு பிரதிநிதித்துவத்தை வழங்குகிறது. இது இந்தியா போன்ற நாடுகளுக்கு மிகவும் முக்கியமானது.
- நெகிழ்வுத்தன்மை : தேவைக்கேற்ப PM-ஐ எளிதாக மாற்ற முடியும் என்பதால் இந்த அமைப்பு நெகிழ்வானது.
Features of Parliamentary Government
- Nominal and Real Executives: The President is the nominal executive (also known as the de jure or titular executive), whereas the Prime Minister is the real executive (de facto executive). As a result, the President is the President of the State, whereas the Prime Minister is the Prime Minister of the Government.
- Double Membership: The Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers serve as the executive, while the Parliament serves as the legislature. Members of parliament elect the Prime Minister and ministers, meaning that the executive comes from the legislative.
- Collective Responsibility: The executive has a collective responsibility to the legislative. There is a collective responsibility, which means that each minister’s responsibilities are shared by the entire Council.
- Secrecy of procedure: A requirement of this type of administration is that cabinet proceedings be kept secret and not made public.
- Prime Ministerial Leadership: The Prime Minister is in charge of this system of administration.
- Majority Party Rule: The Prime Minister is usually appointed by the leader of the party that obtains a majority in the lower chamber.
- Bicameral Legislature: Bicameral legislatures are used in most parliamentary democracies.
- Political Homogeneity: Members of the Council of Ministers are usually from the same political party, and so have similar political ideologies. The ministers in a coalition government are bound by consensus.
- No fixed term: The government’s term is determined by the lower house’s majority support. The council of ministers must resign if the government fails to win a vote of no confidence. There will be elections, and a new government will be formed.
Merits of Parliamentary System
- Better coordination between the administration and the legislature: Since the administration is part of the legislature, and most legislatures generally support the government, it is easier to pass laws and implement them.
- Prevent authoritarianism: since the executive branch is accountable to the legislature and can vote against it with motions of no confidence, there is no authoritarianism. Also, unlike a presidential system, power will not be concentrated in one hand.
- Responsible government: Ministers are accountable to Parliament for their actions. Parliament exercises control over the executive through various devices like question hour, adjournment motion, no-confidence motion etc.
- Ready Alternative Government: If a ruling party loses the majority, president can invite the opposition party to form the government. Therefore alternative government can be formed without fresh elections.
- Representation of different groups: In this system, the parliament provides representation for different groups in the country. This is especially important for countries like India.
- Flexibility: The system is flexible because the PM can be easily changed as needed.
-
Question 20 of 88
20. Question
Who among the following is authorized to certify whether a particular bill is a money bill or not?
பின்வரும் நபர்களில் எவர் ஒருவர், ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட மசோதா பண மசோதாவா இல்லையா என சான்றளிப்பார்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 21 of 88
21. Question
Who among the following was the first speaker of the Indian Parliament?
பின்வருபவருள் எவர் இந்திய பாராளுமன்றத்தின் முதல் சபாநாயகர் ஆவார்?(PYQ)Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect


-
Question 22 of 88
22. Question
Which of the following bills were decided by the joint sitting of the two houses of Parliament?
பின்வருவனவற்றுள் எந்த மசோதாக்கள் பாராளுமன்ற கூட்டுக் கூட்டத்தால் நிறைவேற்றப்பட்டவை?(PYQ)
Correct
அரசியலமைப்பு அடிப்படை:
- இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பின் பிரிவு 108, நாடாளுமன்றத்தின் இரு அவைகளின் கூட்டுக் கூட்டங்களை நடத்துவதற்கு வழிவகை செய்கிறது.
ஜனாதிபதியின் பங்கு:
- இந்தியக் குடியரசுத் தலைவர் நாடாளுமன்றத்தின் கூட்டுக் கூட்டத்தைக் கூட்டலாம்.
தலைமை அதிகாரி:
- கூட்டுக் கூட்டத்திற்கு மக்களவைத் தலைவர் தலைமை தாங்குகிறார்.
Bills Passed Through Joint Sittings:
- Dowry Prohibition Bill, 1961
- Banking Service Commission (Repeal) Bill, 1978
- Prevention of Terrorism Bill, 2002
Incorrect
அரசியலமைப்பு அடிப்படை:
- இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பின் பிரிவு 108, நாடாளுமன்றத்தின் இரு அவைகளின் கூட்டுக் கூட்டங்களை நடத்துவதற்கு வழிவகை செய்கிறது.
ஜனாதிபதியின் பங்கு:
- இந்தியக் குடியரசுத் தலைவர் நாடாளுமன்றத்தின் கூட்டுக் கூட்டத்தைக் கூட்டலாம்.
தலைமை அதிகாரி:
- கூட்டுக் கூட்டத்திற்கு மக்களவைத் தலைவர் தலைமை தாங்குகிறார்.
Bills Passed Through Joint Sittings:
- Dowry Prohibition Bill, 1961
- Banking Service Commission (Repeal) Bill, 1978
- Prevention of Terrorism Bill, 2002
-
Question 23 of 88
23. Question
What is the Quorum of both the houses of Parliament to transact business?
பாராளுமன்றத்தின் ஈரவைகளும் செயல்பட குறைந்தபட்ச உறுப்பினர் எண்ணிக்கை என்ன?(PYQ)
Correct
பாராளுமன்றத்தின் இரு அவைகளும் செயல்பட, அவைகளின் மொத்த உறுப்பினர்களில் 1/10 பங்கு உறுப்பினர்கள் இருக்க வேண்டும். இதுவே கூட்டத்தை தொடங்குவதற்கான குறைந்தபட்ச எண்ணிக்கை ஆகும்.- மக்களவை: 543 உறுப்பினர்கள்.
- மாநிலங்களவை: 245 உறுப்பினர்கள்.
- கூட்டத்தை தொடங்குவதற்கான குறைந்தபட்ச எண்ணிக்கை: 1/10 பங்கு.
- கூட்டுக் கூட்டத்தை அமைப்பதற்கான கோரம்: அவையின் மொத்த உறுப்பினர்களின் எண்ணிக்கையில் 1/10 பங்கு.
Incorrect
-
Question 24 of 88
24. Question
Either House of the Parliament is authorised to declare the seat of a member vacant, who remains absent without permission from all the meetings of that House for a period of
———— நாட்கள்/காலம், ஒரு உறுப்பினர் அனுமதி இன்றி கலந்து கொள்ளாமல் இருந்தால் அந்த இடத்தை காலியிடம் என்று இரண்டு அவைகளும் அறிவிக்கலாம்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 25 of 88
25. Question
What is the name of the Indian parliament?
இந்திய பாராளுமன்றத்தின் பெயர் என்ன?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 26 of 88
26. Question
Which Article of the Indian Constitution has given the President of India to dissolve the house of people?
மக்களவையை கலைக்கும் அதிகாரம் இந்திய ஜனாதிபதிக்கு எந்த அரசியலமைப்பு விதியின் கீழ் அளிக்கப்பட்டது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 27 of 88
27. Question
By which amendment, the tenth schedule was added in the Indian Constitution?
எந்த சட்டத் திருத்தத்தின் மூலம் 10-வது அட்டவணை இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பில் சேர்க்கப்பட்டது?(PYQ)
Correct
1985 ஆம் ஆண்டு, 52வது அரசியலமைப்புத் திருத்தச் சட்டம் மூலம், 10வது அட்டவணை இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பில் சேர்க்கப்பட்டது, இது கட்சித் தாவல் தடுப்புச் சட்டம் என்றும் அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
பிப்ரவரி 15, 1985 அன்று ஜனாதிபதியின் ஒப்புதலைப் பெற்ற அரசியலமைப்பு (ஐம்பத்து-இரண்டாவது திருத்தம்) சட்டம், 1985, 18 மார்ச் 1985 அன்று நடைமுறைக்கு வந்தது.
Incorrect
1985 ஆம் ஆண்டு, 52வது அரசியலமைப்புத் திருத்தச் சட்டம் மூலம், 10வது அட்டவணை இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பில் சேர்க்கப்பட்டது, இது கட்சித் தாவல் தடுப்புச் சட்டம் என்றும் அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
பிப்ரவரி 15, 1985 அன்று ஜனாதிபதியின் ஒப்புதலைப் பெற்ற அரசியலமைப்பு (ஐம்பத்து-இரண்டாவது திருத்தம்) சட்டம், 1985, 18 மார்ச் 1985 அன்று நடைமுறைக்கு வந்தது.
-
Question 28 of 88
28. Question
The budget is presented in the House of the people
மக்களவையில் வரவு செலவு திட்டத்தை சமர்ப்பிப்பவர்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 29 of 88
29. Question
Assertion (A): Court cannot direct legislature to enact a particular kind of law.
Reason (R): Legislation is the exclusive rights of the Legislatures
கூற்று (A): ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட வகை சட்டத்தை இயற்றும்படி நீதிமன்றம் சட்டமன்றத்தை நெறிபடுத்த இயலாது
காரணம் (R): சட்டமியற்றுவது சட்டமன்றங்களின் தனிப்பட்ட முழு உரிமையாகும்.(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 30 of 88
30. Question
The two member constituencies (Abolition) Act was enacted on
இரட்டை உறுப்பினர் தொகுதி ஒழிப்பு சட்டம் இயற்றப்பட்ட ஆண்டு(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 31 of 88
31. Question
Arrange the following stages in the enactment of the Budget in proper order.
1) General discussion
2) Appropriation Bill
3) Finance Bill
4) Voting of the Demands for grant
5) Presentation to legislatureவரவு – செலவு திட்டம் இயற்றுவதில் உள்ள பல்வேறு நிலைகளை முறையாக வரிசைப்படுத்துக (PYQ)
1) பொது விவாதம்
2) ஒதுக்கீட்டு மசோதா
3) நிதி மசோதா
4) மானியக் கோரிக்கை மீதான வாக்கெடுப்பு
5) சட்டமன்றத்தின் சமர்ப்பித்தல்Correct
# Short cut: P G S V A F
The budget goes through the following six stages in the Parliament:- Presentation of budget.
- General discussion.
- Scrutiny by departmental committees.
- Voting on demands for grants.
- Passing of appropriation bill.
- Passing of finance bill
இந்திய பட்ஜெட்டை நாடாளுமன்றத்தில் இயற்றும் செயல்முறை ஆறு முக்கிய கட்டங்களை உள்ளடக்கியது: விளக்கக்காட்சி, பொது விவாதம், துறை குழுக்களின் ஆய்வு, மானியங்களுக்கான கோரிக்கைகள் மீது வாக்களித்தல், ஒதுக்கீட்டு மசோதாவை நிறைவேற்றுதல் மற்றும் நிதி மசோதாவை நிறைவேற்றுதல்
Incorrect
# Short cut: P G S V A F
The budget goes through the following six stages in the Parliament:- Presentation of budget.
- General discussion.
- Scrutiny by departmental committees.
- Voting on demands for grants.
- Passing of appropriation bill.
- Passing of finance bill
இந்திய பட்ஜெட்டை நாடாளுமன்றத்தில் இயற்றும் செயல்முறை ஆறு முக்கிய கட்டங்களை உள்ளடக்கியது: விளக்கக்காட்சி, பொது விவாதம், துறை குழுக்களின் ஆய்வு, மானியங்களுக்கான கோரிக்கைகள் மீது வாக்களித்தல், ஒதுக்கீட்டு மசோதாவை நிறைவேற்றுதல் மற்றும் நிதி மசோதாவை நிறைவேற்றுதல்
-
Question 32 of 88
32. Question
Assertion (A) : The device of Adjournment motion is not used by the Rajya Sabha
Reason (R) : An Adjournment motion does not result in removing the Government from office.
கூற்று (A) : ஒத்திவைப்புத் தீர்மானம் மாநீலங்களவையால் பயன்படுத்தப்படுவது கிடையாது.
காரணம் (R) : ஒத்திவைப்புத் தீர்மானம் அரசாங்கத்தைப் பதவியில் இருந்து அகற்றுவதில்லை(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 33 of 88
33. Question
Which of the statements is correct with reference to The Estimates Committee?
I) Consists of 30 members
II) A Minister is eligible for election
III) The term of the Committee is 2 years
IV) The members are from only Lok Sabhaமதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் வாக்கியங்களை கவனிக்கவும், கீழே குறிப்பிட்டுள்ள வாக்கியங்களில் எது / எவை சரியானவை?(PYQ)
I) 30 உறுப்பினர்களை கொண்டது
II) மத்திய மந்திரி உறுப்பினராக தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படலாம்
III) மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் பதவிக் காலம் 2 வருடம் ஆகும்
IV) உறுப்பினர் அனைவரும் கீழ் சபையில் இருந்துதான் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுவர்.Correct
- மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவில் 30 உறுப்பினர்கள் உள்ளனர். அனைத்து உறுப்பினர்களும் மக்களவையிலிருந்து (கீழ் சபை) தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்பட்டவர்கள். அதாவது மாநிலங்களவையிலிருந்து (மேல் சபை) பிரதிநிதித்துவம் இல்லை. (லோக்சபாவிற்கும் மாநிலங்களவைக்கும் இடையிலான வேறுபாட்டை அறிய, இணைக்கப்பட்ட கட்டுரையைப் பார்க்கவும்.) ஆரம்பத்தில், குழுவில் 25 உறுப்பினர்கள் இருந்தனர், பின்னர் அது 30 ஆக அதிகரிக்கப்பட்டது.
- மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் உறுப்பினர்களைத் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கும் முறைமக்களவை அதன் உறுப்பினர்களிடமிருந்து மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் உறுப்பினர்களைத் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கிறது. தேர்தலின் கொள்கையானது ஒற்றை மாற்றத்தக்க வாக்கு மூலம் விகிதாசார பிரதிநிதித்துவம் ஆகும். மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவில் அனைத்துக் கட்சிகளும் முறையாகப் பிரதிநிதித்துவப்படுத்தப்படுகின்றன.
- மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் உறுப்பினர்களின் பதவிக் காலம்- ஒரு வருடம்மக்களவையால் அதன் உறுப்பினர்களிடமிருந்து தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்பட்ட ஒவ்வொரு உறுப்பினரும் ஒரு வருடத்திற்கு குழுவின் ஒரு பகுதியாக இருப்பார்கள். ஒரு வருடம் கழித்து, ஒரு புதிய தேர்தல் நடைபெற்று உறுப்பினர்கள் மாற்றப்படுவார்கள் அல்லது மீண்டும் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுவார்கள்.
- குறிப்பு : பொது நிறுவனங்கள் குழுவைப் போலவே, ஒரு அமைச்சரை மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் உறுப்பினராகத் தேர்ந்தெடுக்க முடியாது.
- மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் தலைவர்மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் தலைவரை நியமிக்கும் அதிகாரம் மக்களவை சபாநாயகருக்கு உள்ளது. மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் தலைவர் எப்போதும் ஆளும் கட்சியைச் சேர்ந்தவராகவே நியமிக்கப்படுவார். எனவே குழுவில் நியமிக்கப்படும் ஒவ்வொரு தலைவரும் நாட்டின் ஆளும் கட்சியைச் சேர்ந்தவராக இருப்பார்.
Incorrect
- மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவில் 30 உறுப்பினர்கள் உள்ளனர். அனைத்து உறுப்பினர்களும் மக்களவையிலிருந்து (கீழ் சபை) தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்பட்டவர்கள். அதாவது மாநிலங்களவையிலிருந்து (மேல் சபை) பிரதிநிதித்துவம் இல்லை. (லோக்சபாவிற்கும் மாநிலங்களவைக்கும் இடையிலான வேறுபாட்டை அறிய, இணைக்கப்பட்ட கட்டுரையைப் பார்க்கவும்.) ஆரம்பத்தில், குழுவில் 25 உறுப்பினர்கள் இருந்தனர், பின்னர் அது 30 ஆக அதிகரிக்கப்பட்டது.
- மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் உறுப்பினர்களைத் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கும் முறைமக்களவை அதன் உறுப்பினர்களிடமிருந்து மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் உறுப்பினர்களைத் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கிறது. தேர்தலின் கொள்கையானது ஒற்றை மாற்றத்தக்க வாக்கு மூலம் விகிதாசார பிரதிநிதித்துவம் ஆகும். மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவில் அனைத்துக் கட்சிகளும் முறையாகப் பிரதிநிதித்துவப்படுத்தப்படுகின்றன.
- மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் உறுப்பினர்களின் பதவிக் காலம்- ஒரு வருடம்மக்களவையால் அதன் உறுப்பினர்களிடமிருந்து தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்பட்ட ஒவ்வொரு உறுப்பினரும் ஒரு வருடத்திற்கு குழுவின் ஒரு பகுதியாக இருப்பார்கள். ஒரு வருடம் கழித்து, ஒரு புதிய தேர்தல் நடைபெற்று உறுப்பினர்கள் மாற்றப்படுவார்கள் அல்லது மீண்டும் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுவார்கள்.
- குறிப்பு : பொது நிறுவனங்கள் குழுவைப் போலவே, ஒரு அமைச்சரை மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் உறுப்பினராகத் தேர்ந்தெடுக்க முடியாது.
- மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் தலைவர்மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் தலைவரை நியமிக்கும் அதிகாரம் மக்களவை சபாநாயகருக்கு உள்ளது. மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழுவின் தலைவர் எப்போதும் ஆளும் கட்சியைச் சேர்ந்தவராகவே நியமிக்கப்படுவார். எனவே குழுவில் நியமிக்கப்படும் ஒவ்வொரு தலைவரும் நாட்டின் ஆளும் கட்சியைச் சேர்ந்தவராக இருப்பார்.
-
Question 34 of 88
34. Question
The members of Rajya Sabha are elected indirectly. How many members who are distinguished in the field of Art, Literature, Science and Social Service are nominated by the President?
மேலவை உறுப்பினர்கள் மறைமுகமாக தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார்கள். கலை, இலக்கியம், அறிவியல் மற்றும் சமூகப் பணியில் சிறப்பாக பணிபுரிந்த எத்தனை நபர்களை குடியரசு தலைவர் நியமிக்கிறார்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 35 of 88
35. Question
Who one of the following persons is the ex-officio chairman of the Rules Committee, General Purpose Committee and Business Advisory Committee?
பின்வருபவருள் எவர் ஒருவர், விதிமுறைகள் குழு, பொது நோக்கங்கள் மீதான குழு, பணி ஆலோசனைக்குழு ஆசியவற்றின் பதவி வழித்தலைவர் ஆவர்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 36 of 88
36. Question
Which one of the following is not a formally prescribed device available to the members of Parliament?
பாராளுமன்ற உறுப்பினர்களுக்கு பின்வருவனவற்றுள் முறை சார்ந்த கருவியாக இல்லாத நிலையாக இருப்பது எது?(PYQ)
Correct
பாராளுமன்ற உறுப்பினர்களுக்கு முறைசாராத கருவியாக பூஜ்ய நேரம் (Zero Hour) உள்ளது, இது கேள்வி நேரம், அரைமணி நேர விவாதம், குறுகிய கால விவாதம் போன்ற முறை சார்ந்த நேரங்களுக்கு மாறானது.பூஜ்ய நேரம் (Zero Hour):பாராளுமன்றத்தில் உறுப்பினர்கள் தங்களுக்குத் தேவையான கேள்விகளை எழுப்பவும், விவாதிக்கவும் ஒரு முறைசாராத நேரம்.கேள்வி நேரம் (Question Hour):பாராளுமன்றத்தில் உறுப்பினர்கள் கேள்விகள் கேட்கவும், அரசாங்கத்திடம் பதில்கள் பெறவும் ஒதுக்கப்பட்ட நேரம்.அரைமணி நேர விவாதம் (Half-an-hour Discussion):பாராளுமன்றத்தில் ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட விஷயம் பற்றி அரை மணி நேரம் விவாதிக்க ஒதுக்கப்பட்ட நேரம்.குறுகிய கால விவாதம் (Short Duration Discussion):பாராளுமன்றத்தில் ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட விஷயம் பற்றி குறுகிய காலத்தில் விவாதிக்க ஒதுக்கப்பட்ட நேரம்.Incorrect
பாராளுமன்ற உறுப்பினர்களுக்கு முறைசாராத கருவியாக பூஜ்ய நேரம் (Zero Hour) உள்ளது, இது கேள்வி நேரம், அரைமணி நேர விவாதம், குறுகிய கால விவாதம் போன்ற முறை சார்ந்த நேரங்களுக்கு மாறானது.பூஜ்ய நேரம் (Zero Hour):பாராளுமன்றத்தில் உறுப்பினர்கள் தங்களுக்குத் தேவையான கேள்விகளை எழுப்பவும், விவாதிக்கவும் ஒரு முறைசாராத நேரம்.கேள்வி நேரம் (Question Hour):பாராளுமன்றத்தில் உறுப்பினர்கள் கேள்விகள் கேட்கவும், அரசாங்கத்திடம் பதில்கள் பெறவும் ஒதுக்கப்பட்ட நேரம்.அரைமணி நேர விவாதம் (Half-an-hour Discussion):பாராளுமன்றத்தில் ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட விஷயம் பற்றி அரை மணி நேரம் விவாதிக்க ஒதுக்கப்பட்ட நேரம்.குறுகிய கால விவாதம் (Short Duration Discussion):பாராளுமன்றத்தில் ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட விஷயம் பற்றி குறுகிய காலத்தில் விவாதிக்க ஒதுக்கப்பட்ட நேரம். -
Question 37 of 88
37. Question
In which year the Parliament enacted the Official Language Act?
எந்த வருடம் பாராளுமன்றத்தில் அலுவல் மொழி சட்டம் இயற்றப்பட்டது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
Some of the important laws enacted in 1963 are: the Constitution (Sixteenth Amendment) Act, the Equal Remuneration Act, the Limitation Act, the Official Languages Act, and the Central Board of Revenue Act.-
Constitution (Sixteenth Amendment) Act, 1963:An Act enacted to amend Article 19 of the Constitution in order to protect the integrity and sovereignty of the Union.
-
Equal Pay Act 1963:A law enacted with the aim of preventing discrimination in wages on the basis of gender.
-
Limitation Act 1963:An Act to consolidate and amend the law for the limitation of suits and other proceedings and for purposes connected therewith.
-
Official Languages Act, 1963:An Act to provide for the languages to be used for official purposes of the Union, for business transactions in Parliament, for Central and State laws and for certain purposes in the High Courts.
-
Central Board of Revenue Act, 1963:An Act to constitute separate revenue boards for direct taxes and indirect taxes and customs, to confer powers and impose duties on the said boards and to amend certain laws.
-
அரசியலமைப்பு (பதினாறாவது திருத்தம்) சட்டம், 1963:யூனியனின் ஒருமைப்பாடு மற்றும் இறையாண்மையைப் பாதுகாக்கும் விதமாக அரசியலமைப்பின் 19 வது பிரிவை திருத்தியமைக்க இயற்றப்பட்ட சட்டம்.
-
சம ஊதியச் சட்டம் 1963:பாலின அடிப்படையில் ஊதியத்தில் பாகுபாடு காட்டுவதைத் தடுக்கும் நோக்கில் இயற்றப்பட்ட சட்டம்.
-
வரம்புச் சட்டம் 1963:வழக்குகள் மற்றும் பிற நடவடிக்கைகளின் வரம்பு மற்றும் அதனுடன் தொடர்புடைய நோக்கங்களுக்காக சட்டத்தை ஒருங்கிணைத்து திருத்துவதற்க்கான சட்டம்.
-
அதிகாரப்பூர்வ மொழிகள் சட்டம், 1963:யூனியனின் உத்தியோகபூர்வ நோக்கங்களுக்காகவும், பாராளுமன்றத்தில் வணிகப் பரிவர்த்தனைகளுக்காகவும், மத்திய மற்றும் மாநிலச் சட்டங்களுக்காகவும், உயர் நீதிமன்றங்களில் சில நோக்கங்களுக்காகவும் பயன்படுத்தக்கூடிய மொழிகளுக்கு வழங்குவதற்கான சட்டம்.
-
மத்திய வருவாய் வாரியச் சட்டம், 1963:நேரடி வரிகள் மற்றும் மறைமுக வரிகள் மற்றும் சுங்கங்களுக்கான தனி வருவாய் வாரியங்களை அமைப்பதற்கும், அதிகாரங்களை வழங்குவதற்கும், மேற்கூறிய வாரியங்களுக்கு கடமைகளை சுமத்துவதற்கும் சில சட்டங்களைத் திருத்துவதற்கும் இயற்றப்பட்ட சட்டம்.
- யூனியன் பிரதேசங்கள் சட்டம், 1963 பிரிவு 54(3) இன் படி 1 ஜூலை 1963 அன்று பாண்டிச்சேரியின் சட்டமன்றமாக பிரதிநிதித்துவ சபை மாற்றப்பட்டது மற்றும் அதன் உறுப்பினர்கள் சட்டமன்றத்திற்கு தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்பட்டதாகக் கருதப்பட்டது. இவ்வாறு, தேர்தல் இல்லாமல் முதல் சட்டமன்றம் உருவாக்கப்பட்டது.
-
Question 38 of 88
38. Question
Which one of the following Parliamentary Committee is Semi – Judicial in nature ?
கீழ்க்கண்ட பாராளுமன்றக் குழுக்களில் எந்த ஒரு குழு பாதி நீதிபரிபாலன தன்மையுடையது ?(PYQ)
Correct
- Privileges Committee is semi-judicial in nature. This committee examines petitions on general public importance and bills. It also takes representation from associations and individuals for the matters of Union subjects.
- சிறப்புரிமைகள் குழு, பகுதி நீதித்துறை சார்ந்தது. இந்தக் குழு, பொது முக்கியத்துவம் மற்றும் மசோதாக்கள் மீதான மனுக்களை ஆராய்கிறது. யூனியன் பாடங்களின் விஷயங்களுக்கு சங்கங்கள் மற்றும் தனிநபர்களிடமிருந்து பிரதிநிதித்துவத்தையும் பெறுகிறது.
Incorrect
- Privileges Committee is semi-judicial in nature. This committee examines petitions on general public importance and bills. It also takes representation from associations and individuals for the matters of Union subjects.
- சிறப்புரிமைகள் குழு, பகுதி நீதித்துறை சார்ந்தது. இந்தக் குழு, பொது முக்கியத்துவம் மற்றும் மசோதாக்கள் மீதான மனுக்களை ஆராய்கிறது. யூனியன் பாடங்களின் விஷயங்களுக்கு சங்கங்கள் மற்றும் தனிநபர்களிடமிருந்து பிரதிநிதித்துவத்தையும் பெறுகிறது.
-
Question 39 of 88
39. Question
Rajya Sabha consist of
மாநில அவையின் மொத்த உறுப்பினர்கள் எண்ணிக்கை(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 40 of 88
40. Question
Rajya Sabha has equal powers with Lok Sabha
லோக் சபாவிற்கு இணையான அதிகாரத்தை இராஜ்ய சபா பெற்றிருப்பது (PYQ)Correct
Rajya Sabha’s Equal Powers with Lok Sabha:
Constitutional Amendment Bills: Both houses have equal authority in introducing and passing constitutional amendment bills.
Ordinary Bills: Introduction and passage of ordinary bills.
Financial Bills: passage of financial bills involving expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India.
அரசியலமைப்பு திருத்த மசோதாக்கள்: அரசியலமைப்பு திருத்த மசோதாக்களை அறிமுகப்படுத்துவதிலும் நிறைவேற்றுதல்.
சாதாரண பில்கள்: சாதாரண மசோதாக்கள் லோக் சபாவால் நிறைவேற்றப்பட்டாலும், ராஜ்யசபாவும் அதை நிறைவேற்ற வேண்டும்.
நிதி மசோதாக்கள்: (நிதி மசோதாக்கள் லோக் சபையில் மட்டுமே அறிமுகப்படுத்தப்பட முடியும், ஆனால் ராஜ்யசபாவும் அதை நிறைவேற்ற வேண்டும். )
Incorrect
Rajya Sabha’s Equal Powers with Lok Sabha:
Constitutional Amendment Bills: Both houses have equal authority in introducing and passing constitutional amendment bills.
Ordinary Bills: Introduction and passage of ordinary bills.
Financial Bills: passage of financial bills involving expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India.
அரசியலமைப்பு திருத்த மசோதாக்கள்: அரசியலமைப்பு திருத்த மசோதாக்களை அறிமுகப்படுத்துவதிலும் நிறைவேற்றுதல்.
சாதாரண பில்கள்: சாதாரண மசோதாக்கள் லோக் சபாவால் நிறைவேற்றப்பட்டாலும், ராஜ்யசபாவும் அதை நிறைவேற்ற வேண்டும்.
நிதி மசோதாக்கள்: (நிதி மசோதாக்கள் லோக் சபையில் மட்டுமே அறிமுகப்படுத்தப்பட முடியும், ஆனால் ராஜ்யசபாவும் அதை நிறைவேற்ற வேண்டும். )
-
Question 41 of 88
41. Question
Match List I and List Il using codes below
A) Railway Budget – 1) 1950
B) Comptroller and Auditor General – 2) 1921
C) Integrated Financial-Advisor – 3) 1921
D) Public Accounts Committee – 4) 1976பட்டியல் I மற்றும் பட்டியல் II ஆகியவற்றினைக் கீழகண்ட குறியீடுகளைப் பயன்படுத்திப் பொருத்துக (PYQ)
A) ரயில்வே பட்ஜெட் – 1) 1950
B) தலைமை கணக்கு (ம) தணிக்கை அதிகாரி – 2) 1921
C) ஒன்றிணைந்த நிதி ஆலோசகர் – 3) 1921
D) பொதுக் கணக்கு குழு – 4) 1976Correct
1919 ஆம் ஆண்டின் இந்திய அரசாங்கச் சட்டத்தின் விதிகளின் கீழ் 1921 ஆம் ஆண்டில் முதன்முதலில் பொதுக் கணக்குக் குழு அமைக்கப்பட்டது மற்றும் அது இருந்து வருகிறது.
Public Accounts Committee was set up first in 1921 under the provisions of the Government of India Act of 1919 and has since been in existence.
1921 ஆம் ஆண்டில், பிரிட்டிஷ் ரயில்வே பொருளாதார நிபுணர் வில்லியம் அக்வொர்த் தலைமையிலான அக்வொர்த் குழு, ரயில்வே பட்ஜெட்டை பொது அரசாங்க பட்ஜெட்டிலிருந்து பிரிக்க பரிந்துரைத்தது, இது 1924 இல் செயல்படுத்தப்பட்டது, இது இந்தியாவில் ஒரு தனி ரயில்வே பட்ஜெட்டை உருவாக்க வழிவகுத்தது .
In 1921, the Acworth Committee, led by British railway economist William Acworth, recommended separating the railway budget from the general government budget, which was implemented in 1924, leading to the creation of a separate Railway Budget in India.
Incorrect
1919 ஆம் ஆண்டின் இந்திய அரசாங்கச் சட்டத்தின் விதிகளின் கீழ் 1921 ஆம் ஆண்டில் முதன்முதலில் பொதுக் கணக்குக் குழு அமைக்கப்பட்டது மற்றும் அது இருந்து வருகிறது.
Public Accounts Committee was set up first in 1921 under the provisions of the Government of India Act of 1919 and has since been in existence.
1921 ஆம் ஆண்டில், பிரிட்டிஷ் ரயில்வே பொருளாதார நிபுணர் வில்லியம் அக்வொர்த் தலைமையிலான அக்வொர்த் குழு, ரயில்வே பட்ஜெட்டை பொது அரசாங்க பட்ஜெட்டிலிருந்து பிரிக்க பரிந்துரைத்தது, இது 1924 இல் செயல்படுத்தப்பட்டது, இது இந்தியாவில் ஒரு தனி ரயில்வே பட்ஜெட்டை உருவாக்க வழிவகுத்தது .
In 1921, the Acworth Committee, led by British railway economist William Acworth, recommended separating the railway budget from the general government budget, which was implemented in 1924, leading to the creation of a separate Railway Budget in India.
-
Question 42 of 88
42. Question
Who is the ex-officio chairman of the Rajya Sabha?
மாநிலங்களவையில் யார் பதவி வழித்தலைவராக இடம்பெற்று உள்ளார்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 43 of 88
43. Question
Which one of the following Bills must be passed by each house of the Indian parliament separately by special majority?
எவ்வகை மசோதா இந்திய பாராளுமன்றத்தின் இரு அவைகளிலும் தனித்தனியே சிறப்பு பெரும்பான்மையில் நிறைவேற்றப்பட வேண்டும்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 44 of 88
44. Question
A deadlock between the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha calls for a joint sitting of the parliament during a passage of
1) Ordinary Legislation
2) Money Bill
3) Constitution Amendment Bill
பாராளுமன்றத்தின் கூட்டுத்தொடர் எந்த மசோதா கொண்டுவருவதற்கு பயன்படுத்தப்படுகிறது.(PYQ)
1) சாதாரண மசோதா
2) பண மசோதா
3) அரசியலமைப்பு சட்டதிருத்த மசோதாCorrect
Incorrect
-
Question 45 of 88
45. Question
The Report of the Public Accounts Committee is presented in
பொது கணக்குக் குழுவின் அறிக்கை சமர்ப்பிக்கப்படுவது(PYQ)Correct
பொதுக் கணக்குக் குழு (PAC) என்பது ஒரு அரசாங்கத்தின் செலவு மற்றும் நிதிகளை மதிப்பாய்வு செய்யும் சட்டமியற்றுபவர்களின் குழுவாகும் . பொதுப் பணம் சட்டப்பூர்வமாகவும் திறமையாகவும் செலவிடப்படுவதை உறுதி செய்வதற்கான சட்டமன்றத்தின் முயற்சிகளில் PAC ஒரு முக்கிய பகுதியாகும்
- 1919 ஆம் ஆண்டு இந்திய அரசுச் சட்டத்தின் கீழ் 1921 ஆம் ஆண்டு PAC நிறுவப்பட்டது.
நோக்கம்:- அரசாங்கத்தின் வருவாய் மற்றும் செலவினங்களைத் தணிக்கை செய்தல்
- பொது நிதிகள் புத்திசாலித்தனமாகவும் சட்டப்பூர்வமாகவும் பயன்படுத்தப்படுவதை உறுதி செய்தல்.
- வீண் விரயம், இழப்பு, ஊழல் மற்றும் திறமையின்மை வழக்குகளைக் கண்டறியவும்.
Incorrect
பொதுக் கணக்குக் குழு (PAC) என்பது ஒரு அரசாங்கத்தின் செலவு மற்றும் நிதிகளை மதிப்பாய்வு செய்யும் சட்டமியற்றுபவர்களின் குழுவாகும் . பொதுப் பணம் சட்டப்பூர்வமாகவும் திறமையாகவும் செலவிடப்படுவதை உறுதி செய்வதற்கான சட்டமன்றத்தின் முயற்சிகளில் PAC ஒரு முக்கிய பகுதியாகும்
- 1919 ஆம் ஆண்டு இந்திய அரசுச் சட்டத்தின் கீழ் 1921 ஆம் ஆண்டு PAC நிறுவப்பட்டது.
நோக்கம்:- அரசாங்கத்தின் வருவாய் மற்றும் செலவினங்களைத் தணிக்கை செய்தல்
- பொது நிதிகள் புத்திசாலித்தனமாகவும் சட்டப்பூர்வமாகவும் பயன்படுத்தப்படுவதை உறுதி செய்தல்.
- வீண் விரயம், இழப்பு, ஊழல் மற்றும் திறமையின்மை வழக்குகளைக் கண்டறியவும்.
-
Question 46 of 88
46. Question
In Lok Sabha, how many members are elected directly by the people?
மக்களவையில் மக்களால் நேரடியாக தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படும் உறுப்பினர்களின் எண்ணிக்கை யாது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 47 of 88
47. Question
Match the following
A) First session of Constituent Assembly – 1) 4th April 1957
B) Date on which drafting Committee was set up – 2) 13th May 1952
C) 1st sitting of Rajya Sabha – 3) 29th August 1947
D) Dissolution of the 1st Lok Sabha – 4) 9th December 1946பொருத்துக(PYQ)
A) அரசியல் நிர்ணய சபை முதல் – 1) 4 ஏப்ரல் 1957
B) வரைவுக் குழு உருவாக்கப்பட்ட தேதி – 2) 13 மே 1952
C) மாநிலங்கள் அவையின் முதல் கூட்டத்தொடர் – 3) 29 ஆகஸ்ட் 1947
D) முதல் லோக் சபா கலைக்கப்பட்ட நாள் – 4) 9 டிசம்பர் 1946Correct
1952 ஆம் ஆண்டு இந்தியாவின் முதல் பொதுத் தேர்தலுக்குப் பிறகு அமைக்கப்பட்ட முதல் மக்களவை, அதன் முழு ஐந்தாண்டு பதவிக் காலத்திற்குப் பிறகு, ஏப்ரல் 4, 1957 அன்று கலைக்கப்பட்டது.
விளக்கம்:
அரசியலமைப்பு: இந்தியாவின் முதல் பொதுத் தேர்தலைத் தொடர்ந்து, ஏப்ரல் 17, 1952 அன்று முதல் மக்களவை அமைக்கப்பட்டது.
முதல் அமர்வு: மக்களவையின் முதல் கூட்டத்தொடர் மே 13, 1952 அன்று கூடியது.
கலைப்பு: முதல் மக்களவை அதன் முழு ஐந்தாண்டு பதவிக்காலத்தை நிறைவு செய்த பின்னர், ஏப்ரல் 4, 1957 அன்று கலைக்கப்பட்டது.Incorrect
1952 ஆம் ஆண்டு இந்தியாவின் முதல் பொதுத் தேர்தலுக்குப் பிறகு அமைக்கப்பட்ட முதல் மக்களவை, அதன் முழு ஐந்தாண்டு பதவிக் காலத்திற்குப் பிறகு, ஏப்ரல் 4, 1957 அன்று கலைக்கப்பட்டது.
விளக்கம்:
அரசியலமைப்பு: இந்தியாவின் முதல் பொதுத் தேர்தலைத் தொடர்ந்து, ஏப்ரல் 17, 1952 அன்று முதல் மக்களவை அமைக்கப்பட்டது.
முதல் அமர்வு: மக்களவையின் முதல் கூட்டத்தொடர் மே 13, 1952 அன்று கூடியது.
கலைப்பு: முதல் மக்களவை அதன் முழு ஐந்தாண்டு பதவிக்காலத்தை நிறைவு செய்த பின்னர், ஏப்ரல் 4, 1957 அன்று கலைக்கப்பட்டது. -
Question 48 of 88
48. Question
Qualifications for member of parliament is mentioned in Article ———— of Indian constitution
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பின் விதி ———— பாராளுமன்ற உறுப்பினருக்கான தகுதிகளைப் பற்றியதாகும்.(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 49 of 88
49. Question
The Chairman of the Rajya Sabha is elected by
ராஜ்ய சபை தலைவர் இவர்களால் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார்(PYQ)Correct
இந்திய துணைத் தலைவரான ராஜ்யசபாவின் தலைவர், ஒற்றை மாற்றத்தக்க வாக்கு மூலம் விகிதாசார பிரதிநிதித்துவ முறையைப் பயன்படுத்தி, நாடாளுமன்றத்தின் இரு அவைகளின் (லோக்சபா மற்றும் ராஜ்யசபா) உறுப்பினர்களைக் கொண்ட ஒரு தேர்தல் கல்லூரியின் உறுப்பினர்களால் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார் .
The chairman of the Rajya Sabha, who is also the Vice President of India, is elected by the members of an electoral college consisting of the members of both houses of Parliament (Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha) using the system of proportional representation by means of single transferable vote.
Incorrect
இந்திய துணைத் தலைவரான ராஜ்யசபாவின் தலைவர், ஒற்றை மாற்றத்தக்க வாக்கு மூலம் விகிதாசார பிரதிநிதித்துவ முறையைப் பயன்படுத்தி, நாடாளுமன்றத்தின் இரு அவைகளின் (லோக்சபா மற்றும் ராஜ்யசபா) உறுப்பினர்களைக் கொண்ட ஒரு தேர்தல் கல்லூரியின் உறுப்பினர்களால் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார் .
The chairman of the Rajya Sabha, who is also the Vice President of India, is elected by the members of an electoral college consisting of the members of both houses of Parliament (Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha) using the system of proportional representation by means of single transferable vote.
-
Question 50 of 88
50. Question
Public accounts committee consists of
பொது கணக்குக் குழுவின் உறுப்பினர் எண்ணிக்கை(PYQ)Correct
The Public Accounts Committee (PAC) in India consists of not more than 22 members, 15 from the Lok Sabha and 7 from the Rajya Sabha, elected annually by their respective houses.
உறுப்பினர்:
- 15 உறுப்பினர்கள் மக்களவையால் (கீழ் சபை) தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார்கள்.
- 7 உறுப்பினர்கள் மாநிலங்களவையால் (மேல் சபை) தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார்கள்.
- விகிதாசார பிரதிநிதித்துவக் கொள்கையின்படி, ஒற்றை மாற்று வாக்கு மூலம் உறுப்பினர்கள் ஆண்டுதோறும் அந்தந்த வீடுகளால் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார்கள்.
பதவி காலம்: உறுப்பினர்களின் பதவிக்காலம் ஒரு வருடம்.
Incorrect
The Public Accounts Committee (PAC) in India consists of not more than 22 members, 15 from the Lok Sabha and 7 from the Rajya Sabha, elected annually by their respective houses.
உறுப்பினர்:
- 15 உறுப்பினர்கள் மக்களவையால் (கீழ் சபை) தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார்கள்.
- 7 உறுப்பினர்கள் மாநிலங்களவையால் (மேல் சபை) தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார்கள்.
- விகிதாசார பிரதிநிதித்துவக் கொள்கையின்படி, ஒற்றை மாற்று வாக்கு மூலம் உறுப்பினர்கள் ஆண்டுதோறும் அந்தந்த வீடுகளால் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகிறார்கள்.
பதவி காலம்: உறுப்பினர்களின் பதவிக்காலம் ஒரு வருடம்.
-
Question 51 of 88
51. Question
When was the first Lok Sabha held its first meeting after its constitution?
முதலாவது மக்களவை அமைக்கப்பட்ட பிறகு அதன் முதல் கூட்டம் எப்பொழுது நடைபெற்றது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 52 of 88
52. Question
The maximum permissible gap between two sessions of parliament
நாடாளுமன்றத்தில் இரு கூட்டங்களுக்கு இடையில் இருக்கும் கால இடைவளி(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 53 of 88
53. Question
How many members are nominated for Rajya Sabha?
ராஜ்ய சபாவிற்கு ஒதுக்கப்பட்ட பரிந்துரைக்கப்படும் உறுப்பினர்கள் எத்தனை?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 54 of 88
54. Question
Who was the first Chairman of Rajya Sabha?
ராஜ்ய சபையின் முதல் தலைவர் யார்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 55 of 88
55. Question
Match the following and choose the correct answer: [Speaker – Tenure]
A) Mavalankar – 1) 1962 – 67
B) Hukam Singh – 2) 1980 – 1989
C) K.S Hegde – 3) 1952 – 56
D) Bal Ram Jakhar 4) 1977 – 1980கீழ்கண்டவற்றை பொருத்தி சரியான விடை எழுதுக: [சபாநாயகர் – வருடம்](PYQ)
A) மாவுலங்கர் – 1) 1962-67
B) ஹக்கம் சிங் – 2) 1980-1989
C) கே.எஸ். ஹெக்டே – 3) 1952-56
D) பால் ராம் ஜாக்கர் – 4) 1977-1980Correct
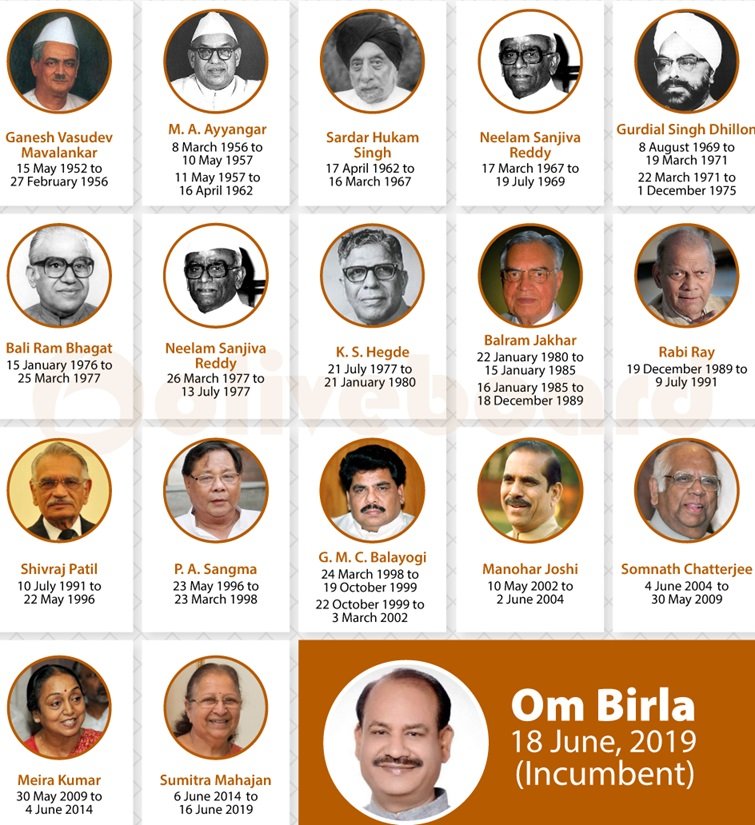 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 56 of 88
56. Question
In 2018, Who is appointed as a chairman of the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) of Parliament?
2018-இல் பாராளுமன்ற பொது கணக்கு கமிட்டியின் தலைவராக நியமிக்கப்பட்டுள்ளவர் யார்?(PYQ)Correct
2025 ல்
The current chairman of the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) of the Indian Parliament is K.C. Venugopal, who took over from Adhir Ranjan Chowdhury in August 2024.
இந்திய நாடாளுமன்றத்தின் பொதுக் கணக்குக் குழுவின் (PAC) தற்போதைய (2025ல்) தலைவர் கே.சி. வேணுகோபால், ஆகஸ்ட் 2024 இல் ஆதிர் ரஞ்சன் சவுத்ரியிடம் இருந்து பொறுப்பேற்றார்.
Incorrect
2025 ல்
The current chairman of the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) of the Indian Parliament is K.C. Venugopal, who took over from Adhir Ranjan Chowdhury in August 2024.
இந்திய நாடாளுமன்றத்தின் பொதுக் கணக்குக் குழுவின் (PAC) தற்போதைய (2025ல்) தலைவர் கே.சி. வேணுகோபால், ஆகஸ்ட் 2024 இல் ஆதிர் ரஞ்சன் சவுத்ரியிடம் இருந்து பொறுப்பேற்றார்.
-
Question 57 of 88
57. Question
Who presides over the meetings of Rajya Sabha?
மாநிலங்களவை கூட்டங்களுக்கு தலைமை தாங்கி நடத்துபவர்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 58 of 88
58. Question
In the Parliamentary form of government the members of the council of ministers are collectively responsible to
பாராளுமன்ற அரசாங்க முறையில் அமைச்சரவையின் உறுப்பினர்கள் யாருக்கு கூட்டுப் பொறுப்புடையவர்கள்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 59 of 88
59. Question
All the expenditure from the consolidated fund in the annual financial statement to be voted by the Lok Sabha are submitted in the form of demand for grants in pursuance of
நிதி தேவைக்காக மக்களவையில் ஆண்டு நிதிநிலை அறிக்கை சமர்ப்பிக்கப்பட்டு ஓட்டெடுப்பு நடத்தி பொது நிதியிலிருந்து அனைத்து செலவுகளையும் செய்வது(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 60 of 88
60. Question
Under which Article of the Constitution of India, joint sitting of both the Houses of Parliament can be convened?
இந்திய அரசமைப்பின் எப்பிரிவின் கீழ் பாராளுமன்றத்தின் ஈரவைகளின் கூட்டு அமர்வு கூட்டப்பட்ட இயலும்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 61 of 88
61. Question
Power to amend the Constitution of India is to be found in
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்புத் திருத்துவதற்கான அதிகாரம் இதில் இடம்பெற்றிருக்கின்றது(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 62 of 88
62. Question
Whose Governments were dismissed in 1984?
I) M.G.Ramachandran
II) S.R.Bommai
III) N.T.Rama Rao
IV) Faroog Abdullaயாருடைய ஆட்சி 1984-ல் கலைக்கப்பட்டது?(PYQ)
I) M.G.ராமச்சந்திரன்
II) S.R.பொம்மை
III) N.T.ராமராவ்
IV) பருக் அப்துல்லாCorrect
Incorrect
-
Question 63 of 88
63. Question
Which of the following are the federal features of the Indian constitution?
1) Rigid Constitution
2) Bicameral Legislature
3) Office of the CAG
4) Collective responsibilityகீழே கொடுக்கப்பட்டுள்ளவைகளில் எவைகள் இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பு கூட்டாட்சி குணாதிசயங்களை கொண்டுள்ளது(PYQ)
1) நெகிழா தன்மையுள்ள அரசியலமைப்பு
2) ஈரவை சட்டமன்றம்
3) இந்திய தலைமைக் கணக்கர் மற்றும் தணிக்கைத் துறை தலைவா்
4) கூட்டு பொறுப்புCorrect
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 64 of 88
64. Question
In a parliamentary system of Government the executive is collectively responsible to the
எது பாராளுமன்ற அரசாங்க முறையில் நிர்வாகத் துறைக்குக் கூட்டு பொறுப்பாகத் திகழ்கிறது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 65 of 88
65. Question
Zero-hour is in practice since
பூஜ்ஜிய-நேரம் நடைமுறைப்படுத்தப்பட்ட ஆண்டு(PYQ)Correct
இந்திய நாடாளுமன்றத்தில், முன்னறிவிப்பு இல்லாமல் அவசர விஷயங்களை நாடாளுமன்ற உறுப்பினர்கள் எழுப்ப அனுமதிக்கும் முறைசாரா நடைமுறையான பூஜ்ஜிய நேரம், 1962 முதல் நடைமுறையில் உள்ளது .
Zero Hour in the Indian Parliament, an informal practice allowing MPs to raise urgent matters without prior notice, has been in practice since 1962
Incorrect
இந்திய நாடாளுமன்றத்தில், முன்னறிவிப்பு இல்லாமல் அவசர விஷயங்களை நாடாளுமன்ற உறுப்பினர்கள் எழுப்ப அனுமதிக்கும் முறைசாரா நடைமுறையான பூஜ்ஜிய நேரம், 1962 முதல் நடைமுறையில் உள்ளது .
Zero Hour in the Indian Parliament, an informal practice allowing MPs to raise urgent matters without prior notice, has been in practice since 1962
-
Question 66 of 88
66. Question
To introduce money bill in parliament, prior permission of ———— is needed
பாராளுமன்றத்தில் பண மசோதாவை அறிமுகப்படுத்த ———— யின் யாருடைய முன் அனுமதி தேவைப்படுகிறது.(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 67 of 88
67. Question
Rajya Sabha is also called the ———— house of the parliament.
இராஜ்ய சபா என்பது பாராளுமன்றத்தின் எந்த அவை?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 68 of 88
68. Question
Which one is the third and important organ of the Government?
அரசாங்கத்தின் மூன்றாவது மற்றும் முக்கியமான அங்கமாகக் கருதப்படுவது எது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 69 of 88
69. Question
One third of the members of the Rajya Sabha retire after every
இராஜ்ய சபாவில் மூன்றில் ஒரு பங்கு உறுப்பினர்கள் ———— முறை ஓய்வு பெறுகின்றனர்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 70 of 88
70. Question
Match the following:
A) Budget session – 1) Lok Sabha
B) Monsoon Session – 2) February
C) Money bill – 3) July
D) Winter session – 4) Novemberபொருத்துக:(PYQ)
A) வரவு செலவு கூட்டத்தொடர் – 1) மக்கள் அவை
B) பருவகாலக் கூட்டத் தொடர் – 2) பிப்ரவரி
C) பண மசோதா – 3) ஜூலை
D) குளிர்காலக் கூட்டத் தொடர் – 4) நவம்பர்Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 71 of 88
71. Question
Assertion (A) : Indian Parliament has a bicameral Legislature.
Reason (R) : Lok Sabha is the Lower house and Rajya Sabha is the Upper house.
கூற்று (A) : இந்திய நாடாளுமன்றம் ஈரவைகளைக் கொண்டதாகும்
காரணம் (R) : கீழ் அவையாக மக்கள் அவையும் மேலவையாக மாநிலங்கள் அவையும் உள்ளன.(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 72 of 88
72. Question
Which of the following committees is not a standing committee of the parliament?
கீழே கொடுக்கப்பட்டுள்ளவைகளில் எது பாராளுமன்றத்தின் நிலைக்குழு கிடையாது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 73 of 88
73. Question
Which of the following is the largest committee of the Parliament?
பாராளுமன்றத்தில் உள்ள குழுக்களில் மிகப்பெரிய குழு எது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 74 of 88
74. Question
The term ‘guillotine’ means that the speaker
‘கில்லட்டின்’ என்னும் சொல்லின் அர்த்தம்; சபாநாயகர்.(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 75 of 88
75. Question
In which one of the following years, General elections to Lok Sabha were not held?
கீழ்க்கண்டவற்றில் எந்த ஆண்டில் மக்களவைப் பொதுத்தேர்தல் நடத்தப்படவில்லை?(PYQ)Correct
 Incorrect
Incorrect

-
Question 76 of 88
76. Question
Who has been appointed as Rajya Sabha TV Editor in Chief?
ராஜ்ய சபாவின் முதன்மை தொலைக்காட்சி ஆசிரியராக நியமிக்கப்பட்டவர் யார் ?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 77 of 88
77. Question
The Committee on Estimates, consisting of 30 members, is constituted by
30 உறுப்பினர்களைக் கொண்ட மதிப்பீட்டுக் குழு உருவாக்கப்படுவது(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 78 of 88
78. Question
The Annual Financial statement of India is prepared under
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பின் எந்த பிரிவின் படி நாட்டின் வருடாந்திர நிதிநிலை அறிக்கை தயார் செய்யப்படுகிறது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 79 of 88
79. Question
The Salary and other emoluments of the speaker and deputy speaker fixed by
சபாநாயகர் மற்றும் துணை சபாநாயகர் ஆகியோரின் ஊதியமும் பிற பணப் பயன்கள் யாரால் நிர்ணயிக்கப்படுகிறது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 80 of 88
80. Question
Who is the first former prime minister to be the leader of opposition in Lok sabha in later years
முதன்முதலில் எந்த முன்னாள் பிரதம மந்திரி, பின்னாளில் லோக்சபாவின் எதிர்கட்சி தலைவராகவும் செயல்பட்டார்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 81 of 88
81. Question
The first joint sitting of the parliament was held in the year
நாடாளுமன்றத்தின் முதல் கூட்டமர்வு நடைபெற்றது(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 82 of 88
82. Question
How many members are elected to Lok sabha from the Union Territory of Delhi ?
யூனியன் பிரதேசமான டெல்லியில் இருந்து மக்களவைக்கு எத்தனை உறுப்பினர்கள் தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்படுகின்றனர் ?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 83 of 88
83. Question
Match the following : [State – No. of Rajya sabha members]
A) Tamilnadu – 1) 16
B) West Bengal – 2) 19
C) Maharashtra – 3) 11
D) Madhya Pradesh – 4) 18
கீழ்க்கண்டவற்றினைப் பொருத்துக [மாநிலங்கள் – மாநிலங்களவை உறுப்பினர் எண்ணிக்கை](PYQ)
A) தமிழ்நாடு – 1) 16
B) மேற்கு வங்காளம் – 2) 19
C) மகாராஷ்டிரா – 3) 11
D) மத்தியப் பிரதேசம் – 4) 18Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 84 of 88
84. Question
The speaker of 17th Lok Sabha is
17வது பாராளுமன்றத்தின் சபாநாயகர்(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 85 of 88
85. Question
Which one of the following statements about a money bill is not correct?
கீழ்க்காணும் கருத்துக்களில் எந்த ஒன்று பண மசோதாக்கள் பற்றி தவறானது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 86 of 88
86. Question
None of the following is a Lok Sabha Session?
பின்வருவனவற்றில் எது மக்களவை கூட்டத்தொடர் அல்ல?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 87 of 88
87. Question
Parliamentary privileges are specified in
பாராளுமன்ற சலுகைகளை ———— ல் குறிப்பிடப்பட்டுள்ளன.(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 88 of 88
88. Question
Who among the following recommends to the parliament for the abolition of the legislative council in a state?
பின்வருவனவற்றில் ஒரு மாநிலக்தின் சட்டமன்ற மேலவை ஒழிக்க பாராளுமன்றத்தால் பரிந்துரை செய்வது(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect