Quiz-summary (or) [Show All Quiz]
0 of 31 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
Information
POLITY-01 Constitution of India (TM/EM)-PYQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 31 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 31
1. Question
which act empowered the Crown to create a board of 6 commissioners for the affairs of India
எந்தச் சட்டம் 6 கமிஷனர்களை கொண்ட வாரியம் இந்திய விவகாரங்களை கவனித்துக் கொள்ள தலைவரை நியமனம் செய்யலாம் எனக் கூறியதுCorrect
1) பிட் இந்தியச்சட்டம் 1784
2) இங்கிலாந்து பிரதமர் வில்லியம் பிட்-என்பவரால் இயற்றப்பட்டது
3) 1781 ஒப்படைப்பு சட்டத்தின் குறைகளைக் களைவதற்காக அமைக்கப்பட்டது.
4) இரட்டை அரசாங்கமுறை நிறுவப்பட்டது.(Established a system diarchy)
5) பிட் இந்தியச் சட்டத்திற்குப் பிறகு முதல் ஆளுநர் ஜெனரல் (Who was the first Governor-General after Pitt’s India Act?)-லார்டு கார்ன்வாலிஸ்
Incorrect
1) பிட் இந்தியச்சட்டம் 1784
2) இங்கிலாந்து பிரதமர் வில்லியம் பிட்-என்பவரால் இயற்றப்பட்டது
3) 1781 ஒப்படைப்பு சட்டத்தின் குறைகளைக் களைவதற்காக அமைக்கப்பட்டது.
4) இரட்டை அரசாங்கமுறை நிறுவப்பட்டது.(Established a system diarchy)
5) பிட் இந்தியச் சட்டத்திற்குப் பிறகு முதல் ஆளுநர் ஜெனரல் (Who was the first Governor-General after Pitt’s India Act?)-லார்டு கார்ன்வாலிஸ்
-
Question 2 of 31
2. Question
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபை யாருடைய முன்மொழிவின் அடிப்படையில் ஏற்படுத்தப்பட்டது
The constituent assembly of India was set up according to the proposal of
Correct
- அமைச்சரவை தூதுக்குழு உறுப்பினர்கள் இந்தியாவிற்கு 1946 மார்ச்சில் வருகை புரிந்தனர்
- உறுப்பினர்கள்(3)- ஸ்டாபோர்டு கிரிப்ஸ் , ஏ வி அலெக்சாண்டர், பெதிக் லாரன்ஸ்
- இக்குழுவின் பரிந்துரையின் அடிப்படையில் 6-12-1946 இல் அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபை உருவாக்கப்பட்டது
- Who headed the Cabinet Mission?கேபினட் மிஷனை யார் தலைமை தாங்கினார்? பெதிக் லாரன்ஸ்
- முதல் கூட்டம் 9 -12 -1946 , இரண்டாம் கூட்டம் 11-12-1946
- The Constituent Assembly proposed by Cabinet Mission would consist of how many members? கேபினட் மிஷன் பரிந்துரைத்த அரசியலமைப்பு சபையில் எத்தனை உறுப்பினர்கள் இருந்தனர்? –389
- Cabinet Mission rejected which demand of the Muslim League? கேபினட் மிஷன் முஸ்லிம் லீக்கின் எந்தக் கோரிக்கையை நிராகரித்தது? –Pakistan உருவாக்கம்
- Cabinet Mission suggested grouping of provinces into how many sections? கேபினட் மிஷன் மாகாணங்களை எத்தனை பிரிவுகளாகக் குழுவாகச் சேர்க்க பரிந்துரைத்தது? –3
- Who was the Viceroy of India during the Cabinet Mission? கேபினட் மிஷன் இந்தியா வந்தபோது வைஸ்ராய் யார்?- லார்டு வேவேல் Lord Wavell
- Which British Prime Minister sent the Cabinet Mission? கேபினட் மிஷனை அனுப்பிய பிரிட்டிஷ் பிரதமர் யார்? -கிளெமெண்ட் அட்லீ
- Which provinces were included in Group A? Group A-வில் எந்த மாகாணங்கள் சேர்ந்தன? -பீஹார், மும்பை, மட்ராஸ், யுபி
- Group B included which provinces? Group B-வில் எந்த மாகாணங்கள்? -பஞ்சாப், சிந்து, பலூச்சிஸ்தான், வடமேற்கு எல்லைப் பிராந்தியம்
- Group C consisted of which provinces? Group C-வில் எந்த மாகாணங்கள் இருந்தன? -பெங்கால், அசாம்
Incorrect
- அமைச்சரவை தூதுக்குழு உறுப்பினர்கள் இந்தியாவிற்கு 1946 மார்ச்சில் வருகை புரிந்தனர்
- உறுப்பினர்கள்(3)- ஸ்டாபோர்டு கிரிப்ஸ் , ஏ வி அலெக்சாண்டர், பெதிக் லாரன்ஸ்
- இக்குழுவின் பரிந்துரையின் அடிப்படையில் 6-12-1946 இல் அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபை உருவாக்கப்பட்டது
- Who headed the Cabinet Mission?கேபினட் மிஷனை யார் தலைமை தாங்கினார்? பெதிக் லாரன்ஸ்
- முதல் கூட்டம் 9 -12 -1946 , இரண்டாம் கூட்டம் 11-12-1946
- The Constituent Assembly proposed by Cabinet Mission would consist of how many members? கேபினட் மிஷன் பரிந்துரைத்த அரசியலமைப்பு சபையில் எத்தனை உறுப்பினர்கள் இருந்தனர்? –389
- Cabinet Mission rejected which demand of the Muslim League? கேபினட் மிஷன் முஸ்லிம் லீக்கின் எந்தக் கோரிக்கையை நிராகரித்தது? –Pakistan உருவாக்கம்
- Cabinet Mission suggested grouping of provinces into how many sections? கேபினட் மிஷன் மாகாணங்களை எத்தனை பிரிவுகளாகக் குழுவாகச் சேர்க்க பரிந்துரைத்தது? –3
- Who was the Viceroy of India during the Cabinet Mission? கேபினட் மிஷன் இந்தியா வந்தபோது வைஸ்ராய் யார்?- லார்டு வேவேல் Lord Wavell
- Which British Prime Minister sent the Cabinet Mission? கேபினட் மிஷனை அனுப்பிய பிரிட்டிஷ் பிரதமர் யார்? -கிளெமெண்ட் அட்லீ
- Which provinces were included in Group A? Group A-வில் எந்த மாகாணங்கள் சேர்ந்தன? -பீஹார், மும்பை, மட்ராஸ், யுபி
- Group B included which provinces? Group B-வில் எந்த மாகாணங்கள்? -பஞ்சாப், சிந்து, பலூச்சிஸ்தான், வடமேற்கு எல்லைப் பிராந்தியம்
- Group C consisted of which provinces? Group C-வில் எந்த மாகாணங்கள் இருந்தன? -பெங்கால், அசாம்
-
Question 3 of 31
3. Question
1773 ஆம் ஆண்டு ஒழுங்குமுறை சட்டம் யாரால் நிறைவேற்றப்பட்டது
the Regulation Act of 1773 was passed by whom ?
Correct
- வங்காளத்தின் ஆளுநர் பதவி வங்காளத்தின் கவர்னர் ஜெனரல் என மாற்றப்பட்டது.(governor of Bengal changed to governor general of Bengal)
- வங்காளத்தின் முதல் கவர்னர் ஜெனரல் வாரான் ஹேஸ்டிங் பிரபு (first governor general of Bengal Lord Warren Hastings)
- சாசன சட்டம் 1833 படி வங்காளத்தின் கவர்னர் ஜெனரல் இந்தியாவின் கவர்னர் ஜெனரலாக மாற்றப்பட்டார். (according to Charter Act of 1833 governor general of Bengal changed to Governor General of India)
- இந்தியாவின் முதல் கவர்னர் ஜெனரல் வில்லியம் பெண்டிங் பிரபு (the first governor general of India Lord William bentick)
Incorrect
- வங்காளத்தின் ஆளுநர் பதவி வங்காளத்தின் கவர்னர் ஜெனரல் என மாற்றப்பட்டது.(governor of Bengal changed to governor general of Bengal)
- வங்காளத்தின் முதல் கவர்னர் ஜெனரல் வாரான் ஹேஸ்டிங் பிரபு (first governor general of Bengal Lord Warren Hastings)
- சாசன சட்டம் 1833 படி வங்காளத்தின் கவர்னர் ஜெனரல் இந்தியாவின் கவர்னர் ஜெனரலாக மாற்றப்பட்டார். (according to Charter Act of 1833 governor general of Bengal changed to Governor General of India)
- இந்தியாவின் முதல் கவர்னர் ஜெனரல் வில்லியம் பெண்டிங் பிரபு (the first governor general of India Lord William bentick)
-
Question 4 of 31
4. Question
ஒழுங்குமுறை சட்டம் உச்ச நீதிமன்றம் எந்த இடத்தில் அமைக்கப்படும் என கூறியது?
Regulating act provided for the establishment of Supreme Court at
Correct
1. ஒழுங்குமுறை சட்டம் 1773 அடிப்படையில் 1774 இல் கொல்கத்தாவில் வில்லியம் கோட்டையில் உச்ச நீதிமன்றம் ஏற்படுத்தப்பட்டது (According to regulating act 1773 Supreme Court was established in the Fort William of Kolkata)
2. ஒரு தலைமை நீதிபதி மற்றும் மூன்று நீதிபதிகள் (contains chief justice and three judges )
3. முதல் தலைமை நீதிபதி சார் எலிஜா இம்பே( the first chief justice are Elijah Impei)
Incorrect
1. ஒழுங்குமுறை சட்டம் 1773 அடிப்படையில் 1774 இல் கொல்கத்தாவில் வில்லியம் கோட்டையில் உச்ச நீதிமன்றம் ஏற்படுத்தப்பட்டது (According to regulating act 1773 Supreme Court was established in the Fort William of Kolkata)
2. ஒரு தலைமை நீதிபதி மற்றும் மூன்று நீதிபதிகள் (contains chief justice and three judges )
3. முதல் தலைமை நீதிபதி சார் எலிஜா இம்பே( the first chief justice are Elijah Impei)
-
Question 5 of 31
5. Question
இந்தியாவில் கிழக்கிந்திய கம்பெனியின் ஆட்சியை முடிவிற்கு கொண்டு வந்த சட்டம் எது?
Name the act which ended the role of British East India company in India
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 6 of 31
6. Question
How many members were nominated by the British in the cabinet mission in 1946
1946 இல் ஆங்கிலேயர்களால் நியமிக்கப்பட்ட அமைச்சரவை தூதுக்குழுவின் உறுப்பினர்கள் எத்தனை பேர்?Correct
- Part A state – These states were the provinces of former governors of the British raj. They were ruled by the state legislature and by a governor.This part includes nine states that are listed as follows-;Assam ,West Bengal,Uttar Pradesh,Madhya Pradesh,East Punjab,Orissa,Bombay ,Bihar and Bombay.
- Part B states- These includes states that where Princely states earlier or groups of Princely states.They are controlled and governed by Rajpramukh.The Rajpramukh is appointed by that President of India and was the ruler of the state .this part contains eight princely states.These states are listed as follows-: Hyderabad, Saurashtra, Mysore, Rajasthan, Travancore – Cochin, Hyderabad,Jammu and Kashmir ,Madhya Bharat ( central India agency )
- Part C – This part contains provinces of Chief commissioners . It also contains some princely states.The Governance and control of Part C states is with the chief commissioner . The chief commissioner is appointed by the President of India.The Part C contains ten states . These states are listed as follows -: Ajmer , Bhopal, Vindhya Pradesh,Tripura , Himachal Pradesh, Bilaspur,Coorg state ,Delhi ,Kutch , Manipur.
- Part D states – The part D states are looked after by the lieutenant governor . The lieutenant governor is appointed by the central government . The only area that is in Part D it is the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்புச் சட்டம் உருவாக்கிய நான்கு மாநிலங்கள் பின்வருமாறு -:
- பகுதி A மாநிலம் – இந்த மாநிலங்கள் பிரிட்டிஷ் ராஜ்ஜியத்தின் முன்னாள் ஆளுநர்களின் மாகாணங்களாக இருந்தன. அவை மாநில சட்டமன்றத்தாலும் ஒரு ஆளுநராலும் ஆளப்பட்டன. இந்த பகுதியில் பின்வருமாறு பட்டியலிடப்பட்டுள்ள ஒன்பது மாநிலங்கள் அடங்கும்-; அசாம், மேற்கு வங்கம், உத்தரப் பிரதேசம், மத்தியப் பிரதேசம், கிழக்கு பஞ்சாப், ஒரிசா, பம்பாய், பீகார் மற்றும் பம்பாய்.
- பகுதி B மாநிலங்கள் – இவற்றில் முன்னர் சுதேச அரசுகள் இருந்த மாநிலங்கள் அல்லது சுதேச அரசுகளின் குழுக்கள் அடங்கும். அவை ராஜ்பிரமுக்கால் கட்டுப்படுத்தப்பட்டு நிர்வகிக்கப்படுகின்றன. ராஜ்பிரமுக் இந்திய ஜனாதிபதியால் நியமிக்கப்படுகிறார், மேலும் அந்த மாநிலத்தின் ஆட்சியாளராக இருந்தார். இந்த பகுதி எட்டு சுதேச அரசுகளைக் கொண்டுள்ளது. இந்த மாநிலங்கள் பின்வருமாறு பட்டியலிடப்பட்டுள்ளன-: ஹைதராபாத், சவுராஷ்டிரா, மைசூர், ராஜஸ்தான், திருவிதாங்கூர் – கொச்சி, ஹைதராபாத், ஜம்மு மற்றும் காஷ்மீர், மத்திய பாரதம் (மத்திய இந்திய நிறுவனம்)
- பகுதி C – இந்தப் பகுதியில் தலைமை ஆணையர்களின் மாகாணங்கள் உள்ளன. இதில் சில சுதேச அரசுகளும் உள்ளன. பகுதி C மாநிலங்களின் நிர்வாகம் மற்றும் கட்டுப்பாடு தலைமை ஆணையரிடம் உள்ளது. தலைமை ஆணையர் இந்தியக் குடியரசுத் தலைவரால் நியமிக்கப்படுகிறார். பகுதி C பத்து மாநிலங்களைக் கொண்டுள்ளது. இந்த மாநிலங்கள் பின்வருமாறு பட்டியலிடப்பட்டுள்ளன -: அஜ்மீர், போபால், விந்தியப் பிரதேசம், திரிபுரா, இமாச்சலப் பிரதேசம், பிலாஸ்பூர், கூர்க் மாநிலம், டெல்லி, கட்ச், மணிப்பூர்.
- பகுதி D மாநிலங்கள் – பகுதி D மாநிலங்கள் லெப்டினன்ட் கவர்னரால் கவனிக்கப்படுகின்றன. லெப்டினன்ட் கவர்னர் மத்திய அரசால் நியமிக்கப்படுகிறார். பகுதி D இல் உள்ள ஒரே பகுதி அந்தமான் மற்றும் நிக்கோபார் தீவுகள் மட்டுமே.
Incorrect
- Part A state – These states were the provinces of former governors of the British raj. They were ruled by the state legislature and by a governor.This part includes nine states that are listed as follows-;Assam ,West Bengal,Uttar Pradesh,Madhya Pradesh,East Punjab,Orissa,Bombay ,Bihar and Bombay.
- Part B states- These includes states that where Princely states earlier or groups of Princely states.They are controlled and governed by Rajpramukh.The Rajpramukh is appointed by that President of India and was the ruler of the state .this part contains eight princely states.These states are listed as follows-: Hyderabad, Saurashtra, Mysore, Rajasthan, Travancore – Cochin, Hyderabad,Jammu and Kashmir ,Madhya Bharat ( central India agency )
- Part C – This part contains provinces of Chief commissioners . It also contains some princely states.The Governance and control of Part C states is with the chief commissioner . The chief commissioner is appointed by the President of India.The Part C contains ten states . These states are listed as follows -: Ajmer , Bhopal, Vindhya Pradesh,Tripura , Himachal Pradesh, Bilaspur,Coorg state ,Delhi ,Kutch , Manipur.
- Part D states – The part D states are looked after by the lieutenant governor . The lieutenant governor is appointed by the central government . The only area that is in Part D it is the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்புச் சட்டம் உருவாக்கிய நான்கு மாநிலங்கள் பின்வருமாறு -:
- பகுதி A மாநிலம் – இந்த மாநிலங்கள் பிரிட்டிஷ் ராஜ்ஜியத்தின் முன்னாள் ஆளுநர்களின் மாகாணங்களாக இருந்தன. அவை மாநில சட்டமன்றத்தாலும் ஒரு ஆளுநராலும் ஆளப்பட்டன. இந்த பகுதியில் பின்வருமாறு பட்டியலிடப்பட்டுள்ள ஒன்பது மாநிலங்கள் அடங்கும்-; அசாம், மேற்கு வங்கம், உத்தரப் பிரதேசம், மத்தியப் பிரதேசம், கிழக்கு பஞ்சாப், ஒரிசா, பம்பாய், பீகார் மற்றும் பம்பாய்.
- பகுதி B மாநிலங்கள் – இவற்றில் முன்னர் சுதேச அரசுகள் இருந்த மாநிலங்கள் அல்லது சுதேச அரசுகளின் குழுக்கள் அடங்கும். அவை ராஜ்பிரமுக்கால் கட்டுப்படுத்தப்பட்டு நிர்வகிக்கப்படுகின்றன. ராஜ்பிரமுக் இந்திய ஜனாதிபதியால் நியமிக்கப்படுகிறார், மேலும் அந்த மாநிலத்தின் ஆட்சியாளராக இருந்தார். இந்த பகுதி எட்டு சுதேச அரசுகளைக் கொண்டுள்ளது. இந்த மாநிலங்கள் பின்வருமாறு பட்டியலிடப்பட்டுள்ளன-: ஹைதராபாத், சவுராஷ்டிரா, மைசூர், ராஜஸ்தான், திருவிதாங்கூர் – கொச்சி, ஹைதராபாத், ஜம்மு மற்றும் காஷ்மீர், மத்திய பாரதம் (மத்திய இந்திய நிறுவனம்)
- பகுதி C – இந்தப் பகுதியில் தலைமை ஆணையர்களின் மாகாணங்கள் உள்ளன. இதில் சில சுதேச அரசுகளும் உள்ளன. பகுதி C மாநிலங்களின் நிர்வாகம் மற்றும் கட்டுப்பாடு தலைமை ஆணையரிடம் உள்ளது. தலைமை ஆணையர் இந்தியக் குடியரசுத் தலைவரால் நியமிக்கப்படுகிறார். பகுதி C பத்து மாநிலங்களைக் கொண்டுள்ளது. இந்த மாநிலங்கள் பின்வருமாறு பட்டியலிடப்பட்டுள்ளன -: அஜ்மீர், போபால், விந்தியப் பிரதேசம், திரிபுரா, இமாச்சலப் பிரதேசம், பிலாஸ்பூர், கூர்க் மாநிலம், டெல்லி, கட்ச், மணிப்பூர்.
- பகுதி D மாநிலங்கள் – பகுதி D மாநிலங்கள் லெப்டினன்ட் கவர்னரால் கவனிக்கப்படுகின்றன. லெப்டினன்ட் கவர்னர் மத்திய அரசால் நியமிக்கப்படுகிறார். பகுதி D இல் உள்ள ஒரே பகுதி அந்தமான் மற்றும் நிக்கோபார் தீவுகள் மட்டுமே.
-
Question 7 of 31
7. Question
Assertion (A): The Indian Councils Act also called Morley – Minto reforms was introduced in 1909.
Reason (R) : Lord Curzon’s imperialistic attitude, autocratic rule and Lack of sympathy for the India and failure to comply with legitimate demands of the Indian people act of 1892கூற்று (A) : மார்லே – மிண்டோ சீர்திருத்தம் என அழைக்கப்படுகின்ற இந்திய கவுன்சில் சட்டம் 1909 ல் ஏற்படுத்தப்பட்டது
காரணம் (R) : கர்சன் பிரபுவின், ஏகாதிபத்தியபோக்கு, தன்னிச்சையான ஆட்சி, இந்தியர்களிடம் கொண்ட இரக்கமின்மை மற்றும் இந்திய மக்களின் நியாயமான வேண்டுகோள்களை நிறைவேற்றத் தவறிய 1892 ம் ஆண்டு சட்டம்Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 8 of 31
8. Question
Match the List I and List Il and select the correct answer by using the codes: (PYQ)
A) Vernacular Press Act of 1878 – 1) Lord Chelmsford
B) Indian Universities Act of 1904 – 2) Lord Curzon
C) Indian Councils Act of 1909 – 3) Lord Lytton
D) Rowlatt Act of 1919 – 4) Lord Mintoபட்டியல் I-ல் உள்ளதை பட்டியல் II-ல் உடன் பொருத்தி சரியான விடையை தேர்ந்தெடுக்கவும்
A) தாய்மாழி பத்திரிக்கை சட்டம் 1878 – 1) செம்ஸ்-போர்டு பிரபு
B) இந்திய பல்கலைக்கழக சட்டம் 1904 – 2) கர்சன் பிரபு
C) இந்திய ஆட்சி சட்டம் 1909 – 3) லிட்டன் பிரபு
D) ரெளலட் சட்டம் 1919 – 4) மிண்டோ பிரபுCorrect
Incorrect
-
Question 9 of 31
9. Question
Who among the following persons moved the largest number of amendments in the constituent Assembly?
பின்வரும் நபர்களில் எவர் ஒருவர் அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபையில் பெரும்பாலான திருத்தங்களை கொண்டுவந்தவர்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 10 of 31
10. Question
Match the following: [Names – Positions]
A) Mahatma Gandhi – 1) First Prime Minister
B) Jawaharlal Nehru – 2) Father of Nation
C) Dr.Babu Rajendra Prasad – 3) Chairman of drafting Committee
D) Dr.B.R.Ambedkar – 4) Chairman, Constituent Assemblyசரியான விடையை தேர்ந்தெடுக்க: [பெயர்கள் – பதவிகள்] (PYQ)
A) மகாத்மா காந்திஜி – 1) முதல் பிரதம மந்திரி
B) ஜவஹர்லால் நேரு – 2) தேசப் பிதா
C) டாக்டர் பாபு இராஜேந்திர பிரசாத் – 3) வரைபடக் குழுவின் தலைவர்
D) டாக்டர் B.R.அம்பேத்கார் – 4) அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபையின் தலைவர்Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 11 of 31
11. Question
The duration of the National Anthem is approximately _______ seconds.
தேசிய கீதம் பாடுவதற்கு எடுத்துக் கொள்ள வேண்டிய நேரம் சுமார் ______விநாடிகளாகும். (PYQ)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 12 of 31
12. Question
On which date the objective Resolution was adopted by the Constituent Assembly?
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபை எந்நாளில் குறிக்கோள்கள் அடங்கிய தீர்மானத்தை ஏற்றுக் கொண்டது? (PYQ)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 13 of 31
13. Question
Name the chairman of the States Committee of Constituent Assembly
அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபையில் மாநிலங்களுக்கான குழுவின் தலைவராக இருந்தவர் (PYQ)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 14 of 31
14. Question
Consider the following statements with reference to constituent assembly. Which of the statements is correct ?
I) Mahatma Gandhi is not a member of Constituent Assembly
II) Dr. Rajendra Prasad was elected as President on December 11, 1946
III) Under the Cabinet Mission’s provisions, Constituent Assembly was established
lV) Constituent Assembly executed only the National Flag not the National Anthemஇந்திய அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபையின் வாக்கியத்தை கவனிக்கவும். கீழே குறிப்பிட்டுள்ள வாக்கியங்களில் எது / எவை சரியானவை? (PYQ)
I) மகாத்மா காந்தி இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபையின் உறுப்பினர் அல்லர்
II) அரசியல் நிர்ணய சபையின் தலைவராக டாக்டர் இராஜேந்தீர பிரசாத் டிசம்பர் 11, 1946 தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்பட்டார்.
III) அரசியல் நிர்ணய சபை, கேபினட் மிஷன் தீர்மானத்தால் உருவாக்கப்பட்டது.
IV) தேசிய கொடியை மட்டும் அரசியல் நிர்ணய சபை ஏற்றுக் கொண்டது. தேசிய கீதத்தை ஏற்றுக் கொள்ளவில்லைCorrect
Incorrect
-
Question 15 of 31
15. Question
Who headed the interim cabinet formed in the year 1946?
1946 ல் இடைக்கால அரசாங்கத்திற்கு தலைமை வசித்தவர் யார்? (PYQ)Correct
இந்த அரசாங்கம் செப்டம்பர் 2, 1946 அன்று உருவாக்கப்பட்டது
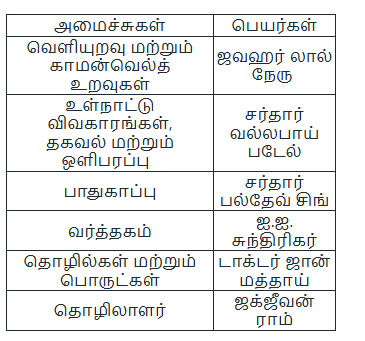 Incorrect
Incorrect
இந்த அரசாங்கம் செப்டம்பர் 2, 1946 அன்று உருவாக்கப்பட்டது

-
Question 16 of 31
16. Question
The constitution of India was drafted by ———— that started working on December 9, 1946
டிசம்பர் 9, 1946 ஆம் ஆண்டு இந்திய அரசியல் அமைப்பை வரையறை செய்ய __________ பணியைத் துவக்கியது.(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 17 of 31
17. Question
The constitution of India came into force on
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பு நடைமுறைக்கு வந்த ஆண்டு(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 18 of 31
18. Question
The constitution of India was framed by the constituent assembly
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பை உருவாக்க அரசியல் நிர்ணய சபை எடுத்துக் கொண்ட காலம்Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 19 of 31
19. Question
Name of the First Law Minister of India_______
இந்தியாவின் முதல் சட்ட அமைச்சராக பொறுப்பேற்றவர் யார்? (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 20 of 31
20. Question
Who wrote the book “The Indian Constitution, Cornerstone of a Nation”?
“இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பின்: தேசத்தின் மூலைக்கல்” என்ற நூலை எழுதியவர் யார்? (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 21 of 31
21. Question
Which is the National song of India?
இந்தியாவில் தேசிய பாடல் எது?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 22 of 31
22. Question
Who was the Chairman of the Constituent Assembly?
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபையின் தலைவராக செயல்பட்டவர் (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 23 of 31
23. Question
Who was the chairman of the drafting committee of the constituent assembly?
அரசியல் நிர்ணய சபையின் வரைவுக் குழு தலைவர் (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 24 of 31
24. Question
Which one of the following persons was selected as the President temporarily at the first session of constituent assembly?
பின்வரும் நபர்களில் எவர் அரசியல் அமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபையின் தற்காலிக தலைவராக முதல் கூட்டத்தில் தோ்ந்தெடுக்கப்பட்டவர்? (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 25 of 31
25. Question
When was the Indian Constitution adopted by the Constituent Assembly?
இந்திய அரசமைப்பு எப்பொழுது அரசமைப்பு பேரவையில் ஏற்றுக் கொள்ளப்பட்டது? (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 26 of 31
26. Question
On which day Jawaharlal Nehru hoisted the tricolour of Indian Independence on the banks of the River Ravi at Lahore?
ஜவஹர்லால் நேரு எந்த நாளில் ராவி நதிக்கரையிலுள்ள லாகூரில் இந்திய சுதந்திர மூவர்ணக் கொடியை ஏற்றினார்? (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 27 of 31
27. Question
In which year the constituent assembly elected its permanent Chairman?
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபையின் நிரந்தர தலைவர் எந்த ஆண்டு தேர்ந்தெடுக்கப்பட்டார்? (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 28 of 31
28. Question
When does India observe its constitution day?
இந்திய அரசியல் அமைப்பு தினம் எப்போது கொண்டாடப்படுகிறது.(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 29 of 31
29. Question
How many members signed the Indian Constitution?
இந்திய அரசியலமைப்பில் எத்தனை உறுப்பினர்கள் கையெழுத்திட்டார்கள்?(PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 30 of 31
30. Question
The Constituent Assembly took the following time in preparing the constitution
அரசியலமைப்பு சட்டத்தை இயற்றுவதற்கு அரசியலமைப்பு நிர்ணய சபை எடுத்துக் கொண்ட கால அளவு (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 31 of 31
31. Question
The constituent Assembly adopted the National Anthem on
அரசியல் நிர்ணயச் சபையால் தேசிய கீதம் ஏற்றுக்கொள்ளப்பட்ட நாள் (PYQ)Correct
Incorrect